Binance has grown into the world’s largest cryptocurrency exchange, recording over 230 million active users in 2025. One of the exchange’s key products is the BNB Smart Chain (BSC) (previously called the Binance Smart Chain), an open-source smart contract platform which allows people to partake in DeFi. This guide will show you what the BNB Smart Chain is all about and how to take advantage of its features.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
► BNB Smart Chain (BSC) is a blockchain that offers a smart contract platform with low transaction fees and compatibility with Ethereum’s EVM.
► BSC utilizes a proof-of-staked-authority (PoSA) consensus mechanism for energy efficiency and network security, combining elements of proof-of-stake and proof-of-authority.
► BSC supports popular decentralized applications (DApps) like PancakeSwap and Venus, which provide users access to yield farming, stablecoin lending, and borrowing.
► BNB Smart Chain’s future relies heavily on Binance’s regulatory standing, but remains popular for its speed and cost-efficiency.
What is the BNB Smart Chain?
BNB Smart Chain (BSC) represents the second generation of blockchain technology. Bitcoin (BTC), Litecoin (LTC), Dogecoin (DOGE), and others are the first generation of blockchains; they hold the sole purpose of producing one product — digital money.
In contrast, BNB Smart Chain is a generalizable blockchain platform for deploying smart contracts and decentralized applications. These automated pieces of code can codify most conceivable logic, including traditional banking services — exchanges, borrowing, and lending.
On a technical level, BSC’s smart contract development is possible thanks to the EVM — Ethereum Virtual Machine. Just like there are engines in the video gaming industry that power games, such as Unreal Engine or Source, so there are engines behind decentralized networks.
EVMs execute smart contracts dispersed across thousands of computers — network nodes.
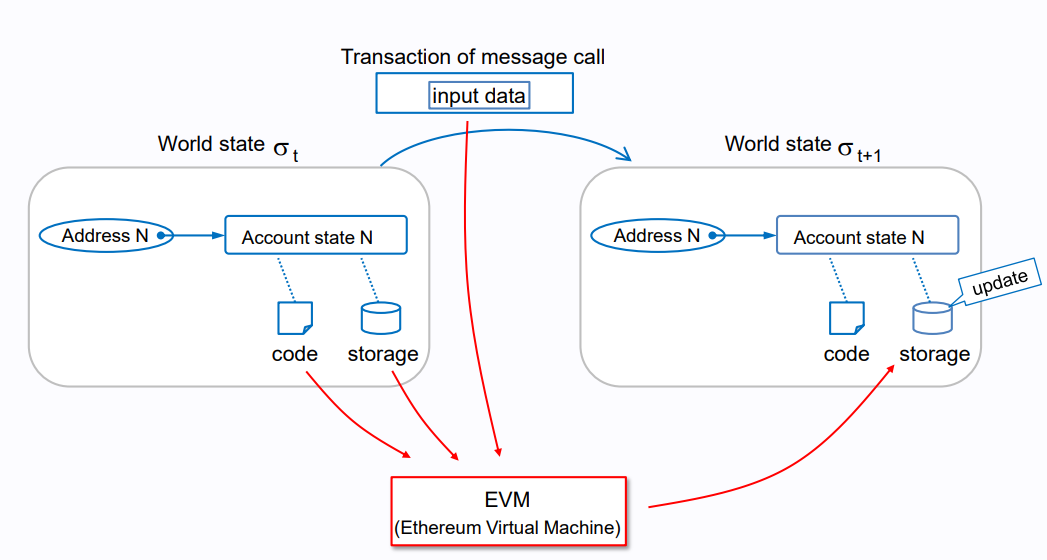
Because of this shared EVM legacy, BSC can easily support smart contracts written on other EVM-compatible blockchains. Once again, this is analogous to the porting of a PC game to PlayStation or Xbox and vice-versa.
Binance Chain vs. Binance Smart Chain
The BNB Smart chain has been through a number of iterations over the years. Here’s a quick timeline of the blockchain’s evolution.
Binance deployed the Binance Chain or BC Chain (eventually called the BNB Chain) in April 2019 in order to facilitate near-instantaneous trading.
The trade-off for this ultra transaction speed was the lack of smart contract programmability. Because smart contracts require a much greater degree of computational power, Binance made a decision to launch a specialized fast-trading blockchain network first.
At this time, Ethereum faced many such congestions, particularly when NFTs emerged onto the scene. For instance, when people rushed to collect and trade CryptoKitties (cartoon cats as NFTs), the entire Ethereum network halted to a standstill in December 2017.
To combat these inevitable congestion issues, Binance launched the Binance Smart Chain in September 2020 as a BC sidechain.
BSC is fully compatible, allowing the migration of crypto assets from one chain to another.
While Binance Smart Chain supported the BEP-20 token standard, Binance Chain supported the BEP-2 token standard. Just as is the case with Ethereum’s ERC-20 token standard, BEP-20 focuses on the easy deployment of tokens.
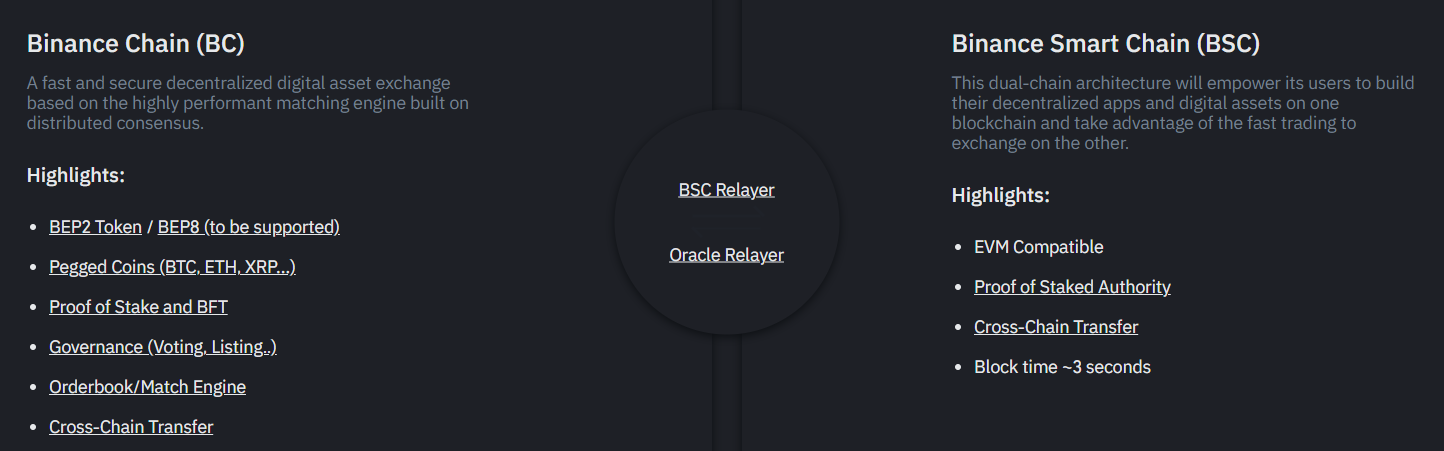
It is important to point out that the Binance Chain (BNB Chain) is a hard fork of Ethereum, while the BSC chain was built using the Cosmos SDK.
In 2022, the BNB Chain merged with the BSC to form the BNB Smart Chain (BSC). This merge is similar to the one that Ethereum underwent.
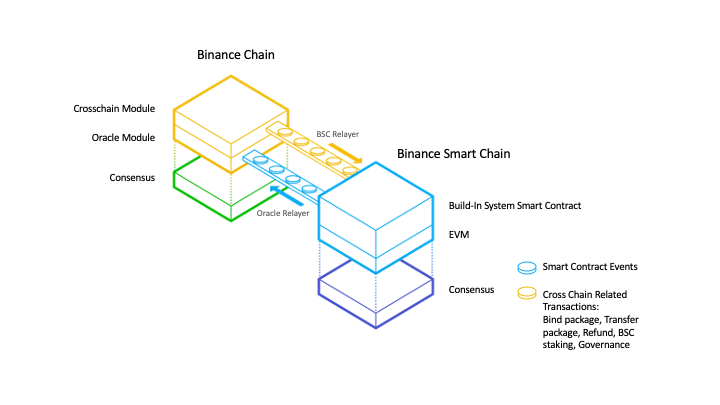
As a result, the BNB Chain became the beacon chain, and BSC became the execution layer for smart contracts. However, in 2024 the BNB Chain was deprecated altogether.
How does BSC work?
As a second-generation blockchain, BSC uses the proof-of-staked-authority (PoSA) algorithm. This means that it combines delegated proof-of-stake (PoS) with proof-of-authority (PoA). This makes BSC much more energy-efficient than first-generation blockchains relying on proof-of-work (PoW), such as Bitcoin.
PoS removes such energy baggage by using economic staking — validators — instead of computational power — miners — to confirm transactions and add new data blocks.
Delegated proof-of-stake
A delegated PoS is a further step up by introducing voting and delegation mechanisms so that those with the most staking power don’t dominate the entire network.
Almost all newer smart contract blockchains use some PoS derivation — Cardano, Algorand, Solana, Avalanche, Cosmos, etc. PoS has become popular not only because it removes miners but also because it relies on an incentive structure to secure the network.
Proof-of-authority
Those with the most stake (tokens locked in) receive greater rewards to preserve the network. However, because it may happen that stakes of equal size have different values, developers made use of proof-of-authority for additional security. PoA simply replaces the monetary value with the validator’s identity.
Lastly, when BSC needs an upgrade or a patch, it enters an epoch period consisting of 240 blocks (about 20 minutes). As another PoS property to curtail malicious behavior — e.g., double signing and node downtime — BSC also employs a “slashing” governance mechanism, which removes a significant portion of a validator’s stake.
BSC gas fees compared to Ethereum
Because blockchains are decentralized networks without centralized oversight, that doesn’t mean they are free to use. Anytime a validator processes a transaction, their reward comes from transaction or gas fees, denominated in gwei as a one-billionth denomination of ETH (1 gwei = 0.000000001 ETH). If we compare BSC with Ethereum, the former is far more affordable.
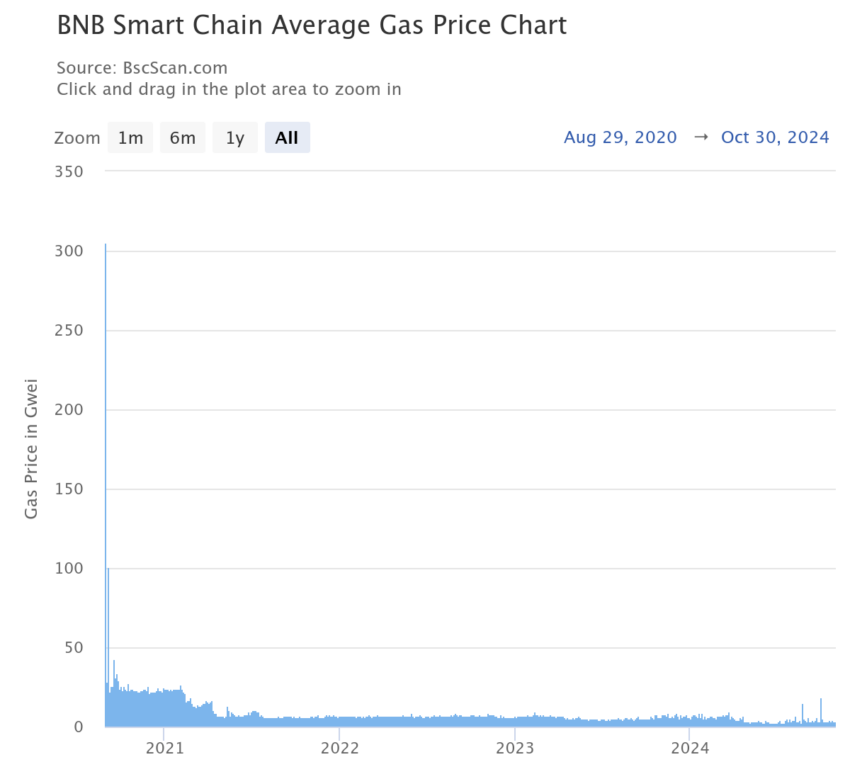
As you can see in the chart above, gas fees on BSC are typically below three gwei, as opposed to Ethereum, which can be as high as 20 gwei, more or less. Additionally, these are just the base fees — those that don’t include more complex transactions involved with DeFi protocols.
BSC tokenomics
What ETH is to Ethereum, Binance Coin (BNB) is to BNB Smart Chain. Holders can use the asset to pay transaction and trading fees on the Binance exchange itself, including the Binance decentralized exchange (DEX).
The native BSC cryptocurrency launched during the July 2017 ICO as an ERC-20 token, less than two weeks before Binance launched. Initially, one could get 2,700 BNB for a single ETH or 20,000 BNB for a single BTC.
BNB has a maximum token supply of 200 million BNB coins. Out of that supply, about 145 million are in circulation. When it comes to Binance Coin inflation, the supply undergoes quarterly (every three months) burning — removing tokens from circulation — with the aim to eventually halve the total supply to 100 million BNB.
Therefore, BNB mirrors Bitcoin’s deflationary nature, with the exception that a highly centralized for-profit company manages it. Binance controls or owns at least 50% of BNB supply.
The founding members received around 80 million BNB (40%), with angel investors receiving another 10%. Correspondingly, the fate of Binance will closely determine the fate of the BNB cryptocurrency.
This is not a comforting thought considering Binance is often a target of regulatory agencies across the world, in addition to accusations of engaging in insider trading. Should Binance be the target of an investigation or the center of a scandal, the price of BNB could significantly drop.
Before Binance launched Binance Chain, BNB started as an ERC-20 token on its competitor chain in 2017 — Ethereum.
BSC staking rewards
Staking is the key to achieving a passive income on the BSC blockchain. If you choose to, you can become a BSC validator to make that happen. However, the requirements are rather high:
- Minimum stake of 10,000 BNB.
- A 64-bit Virtual Private Server (VPS) with a minimum configuration of 16 GB RAM, 500 GB storage space, and 1Gbps fiber internet connection for running a full node (entire copy of BSC blockchain).
In return for securing the network and handling transactions, you will receive a BSC APY (annual percentage yield) of around 13%. Needless to say, not many can afford the privilege of securing BSC.
Lastly, due to the aforementioned slashing mechanism, the validator could be sent to “jail” if the stake in the form of a self-bond falls under 10,000 BNB. This means that the validator’s ability to process transactions and receive rewards will be suspended for one day.
Likewise, downtime and double-signing can earn slashing as well. Downtime happens when a validator misses at least 50 blocks or around 52 minutes. As for double-signing, if a validator attempts to verify two blocks of the same height, they will lose 10,000 BNB and be permanently jailed.
DeFi on BNB Smart Chain
Smart contracts are the foundation for decentralized finance (DeFi). In turn, the front web face to access smart contracts on blockchains is a decentralized application.
Furthermore, like tokens power smart contracts running on the blockchain, blockchain governance and incentive structures run on native tokens, too. As we noted previously, the native token for BNB Smart Chain is Binance Coin (BNB) using the BEP-2 template. On the other hand, all the DApps use the BEP-20 standard.
As far as the most popular DApps on BSC, a very useful tool to use is DappRadar to get the full list across different categories. Here are some of the most popular.
1. PancakeSwap
As a decentralized exchange (DEX), PancakeSwap successfully replicated Ethereum’s Uniswap. It uses an automated market maker (AMM) to facilitate token swapping without centralized oversight.
After it launched in September 2020, its governance token CAKE skyrocketed in value.
Be sure to check this guide on how to stake CAKE tokens to earn passive-yield farming income.
2. BakerySwap
For some reason, BSC DApp developers do love to use baking monikers! BakerySwap is also an AMM, just like Uniswap and PancakeSwap, but with a unique twist. Alongside yield farming for your service as a liquidity provider, BakerySwap adds NFTs on top.
When you earn BAKE tokens, you can put them to good use as a randomly generated combo meal in the form of an NFT. Then, this unique NFT collectible can be further staked to earn more BAKE tokens.
3. Venus
You may have noticed that decentralized finance depends on stablecoins. Because we don’t live in a world where most people use cryptocurrencies for daily expenses, stablecoins are the bridge between DeFi and traditional finance.
The problem is, it is often the case that a single company runs a stablecoin — including the most popular ones like USDT, BUSD, and USDC. This doesn’t quite contribute to DeFi being decentralized.
Venus protocol steps in with the cutting-edge algorithmic stablecoin, VAI, collateralized by a basket of stablecoins and other crypto assets. Furthermore, Venus allows you to tokenize assets and create a money market for lending and borrowing.
Effectively, this makes Venus a unique combo of Compound or Aave with MakerDAO, but exclusive to BNB Smart Chain.
Best crypto wallets for BNB Smart Chain (BSC)

Here are some of the most convenient ways to access the rich BSC DApp ecosystem, which has been popular due to negligible gas fees.
- MetaMask — The top-rated noncustodial wallet that integrates into your web browser and then connects to any DApp. Follow this complete guide to using MetaMask. Focusing on its wide adoption rate, MetaMask also offers support for integrating the most popular Trezor and Ledger hardware wallets.
- Trust Wallet — Bought by Binance, Trust Wallet introduced staking all the way back in 2019. As an integrated DApp browser, it is available for both iOS and Android.
- SafePal — For extra security, SafePal S1 is a compatible hardware wallet. At a price tag of around $50, this is a great way to use cold storage to make your crypto funds hacker-proof. SafePal supports multiple blockchains and more than 10,000 tokens.
- Math Wallet — Like MetaMask, Math Wallet is an extension for the most popular browsers — Chrome, Brave, Edge, etc. Math Wallet has a mission to serve as a universal blockchain wallet, allowing for multichain DApps. If you have heard of a public blockchain, Math Wallet supports it. In addition the wallet has a staking aggregator in the form of MathVault and MathChain as a layer-2 scalability solution based on Substrate.
| Wallet | Type | Platform | Browsers |
|---|---|---|---|
| MetaMask | Hot | Mobile and browser extension | Opera, Firefox, Edge, and Chromium browsers |
| Trust Wallet | Hot | Mobile and browser extension | Chrome, Brave, Opera, Edge |
| SafePal | Hot and cold | Mobile and hardware | Chrome, Edge, and Firefox |
| Math Wallet | Hot | Mobile, browser extension, and cloud | Chrome, Brave, Edge |
What’s the future for BNB Smart Chain?
The BNB Smart Chain has experienced numerous iterations and transformations. As the key network for the largest crypto exchange in 2025, the network’s prominence and role within wider decentralized ecosystems is demonstrable. However, the BNB Smart Chain’s greatest strength is also its key weakness. Among public blockchains, the BNB Smart Chain ranks among the most popular. However, its longevity depends much on how regulators treat Binance and how the company itself conducts its business affairs.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Investing in any cryptocurrency, including BNB, carries risk.
Frequently asked questions
What tokens are on BNB Smart Chain?
What wallets support BNB Smart Chain?
How do I get a BNB Smart Chain wallet address?
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, the educational content on this website is offered in good faith and for general information purposes only. BeInCrypto prioritizes providing high-quality information, taking the time to research and create informative content for readers. While partners may reward the company with commissions for placements in articles, these commissions do not influence the unbiased, honest, and helpful content creation process. Any action taken by the reader based on this information is strictly at their own risk. Please note that our Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers have been updated.




