The Monero network allows users to execute transactions without revealing their identities, transaction history, or exact sums. The network and its native crypto, XMR, offer a secure haven for those looking for privacy in an era marked by increasing scrutiny and documentation of financial transactions. This guide will walk you through everything you need about the network, its operational principles, the native Monero crypto, and its role within the wider crypto sector.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
• Monero is a privacy-focused cryptocurrency that ensures fully anonymous and untraceable transactions.
• It ensures anonymity through stealth addresses, ring signatures, and RingCT.
• XMR’s privacy features boost its utility and popularity in the crypto space.
• Monero’s strong privacy features have made it a target of increased government scrutiny.
What is Monero?
Monero is an open-source cryptocurrency that prioritizes privacy and champions censorship resistance. Unlike better-known cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, Monero utilizes advanced technologies to safeguard user privacy, ensuring that transactions remain confidential and untraceable.
This unique feature makes Monero the sole major cryptocurrency where users enjoy automatic, by-default anonymity.
All transactions on Monero are confidential and untraceable. This anonymity is achieved through three key technologies: Stealth Addresses, Ring Signatures, and RingCT, which hide the sender, receiver, and transaction amount.
History of Monero crypto
Monero’s history is closely tied to Bitcoin. The network originated in 2012 as a fork of Cryptonote, a project created to improve privacy in the cryptosphere and, in particular, address what the founders saw as Bitcoin’s limitations. The idea was that Crytponote could make cryptocurrency transactions unlinkable and untraceable, akin to traditional cash transactions.
“Classic Bitcoin addresses, once being published, become unambiguous identifier for incoming payments, linking them together and tying to the recipient’s pseudonyms. If someone wants to receive an “untied” transaction, he should convey his address to the sender by a private channel.
— Nicolas van Saberhagen: Cryptonote v2.0 Whitepaper
[…] If he wants to receive different transactions which cannot be proven to belong to the same owner he should generate all the different addresses and never publish them in his own pseudonym. We propose a solution allowing a user to publish a single address and receive unconditional unlinkable payments.”
Originally named Bit Monero (“monero” implies coin in Esperanto), the network was forked and renamed Monero after it lost community trust. This erosion of confidence stemmed from some questionable actions by the network’s development team, including the stealthy pre-mining of a significant portion of the coin supply.
Like Bitcoin’s enigmatic Satoshi Nakamoto, Monero’s developers remain largely anonymous, using pseudonyms.
The original Monero developers didn’t act as proprietors of the network. They handed it over to the community for ongoing development and support.
While the majority of the team’s identities remain unknown, a confirmed member of the founding team is Riccardo Spagni (aka @FluffyPony) — who, in March 2023, was forced to deny claims posted on X that he had been working as an informant for Interpol.
How does Monero work?
Monero operates on a proof-of-work consensus mechanism, meaning it depends on miners solving complex computational algorithms to confirm transactions and introduce new blocks on the mainnet.
The platform is built on open-source CryptoNote code, forming the basis of some lesser-known cryptos. Let’s look at the main technologies that keep Monero transactions private.
- Stealth addresses: Monero incorporates the concept of stealth addresses to boost privacy. These addresses enable unique, one-time public addresses for each recipient, ensuring each transaction has a unique public address that cannot be linked to the recipient.
Despite this, the recipient can publish only one inward address while sending all their transactions to unique addresses on the blockchain.
- Ring signatures: Monero uses ring signatures to obscure the identities of those involved in transactions. When a transaction takes place, the outside observer can only see a pool of potential senders, making it impossible to pinpoint the actual sender.
This powerful feature makes Monero transactions truly private.
These privacy-enhancing technologies work together to shield Monero transactions from public scrutiny. Notably, they offer anonymity and improve fungibility.
What makes Monero unique?
Monero introduced several key features and upgrades to ensure privacy, anonymity, and functionality. These include stealth addresses, ring signatures, and additional technologies such as:
- Tail emission: A perpetual emission of coins to ensure sustainability without excessive inflation.
- Ring CT (Ring Confidential Transactions): This technology conceals transaction amounts.
- Bulletproofs: Introduced in 2018 or 2019, bulletproofs significantly reduced transaction sizes and fees.
- RandomX: An egalitarian mining algorithm that promotes fair distribution by emphasizing “one CPU, one vote.”
- Easy mining process: Monero’s key advantage lies in its strong commitment to decentralization, particularly in its mining process. Unlike Bitcoin, which relies on expensive specialized machines (ASICs) for mining, Monero primarily uses regular CPUs found in everyday computers. This approach makes mining more accessible to ordinary individuals and helps prevent centralization and potential network vulnerabilities.
How Monero differs from Bitcoin
To grasp Monero’s significance, it’s important to understand how it differs from Bitcoin, the pioneering cryptocurrency.
- Absolute privacy: Monero distinguishes itself from Bitcoin by offering complete privacy and anonymity in transactions. Unlike Bitcoin, which has some traceability and transaction history tagging, Monero ensures that all transactions remain confidential and untraceable.
- Block size: Monero employs a flexible approach to block sizes. This is unlike Bitcoin’s fixed limit, which could eventually lead to increased transaction fees. Monero allows block sizes to increase as needed to avoid network congestion. Monero imposes penalties for excessively large blocks to prevent abuse, which helps ensure smoother network operation.
- Decentralization: Monero promotes a higher level of decentralization through its mining mechanism. Unlike Bitcoin, which relies on specialized ASICs, Monero mining primarily uses common CPUs, making it accessible to average users. This decentralization reduces the risk of centralization and enhances network robustness and resilience against potential adversarial interests.
- Fungibility: Unlike Bitcoin, Monero coins are indistinguishable and untraceable, ensuring full fungibility. This appeals to users who value the privacy and fungibility of their currency, as every Monero coin has the same value and history.
Monero vs. Bitcoin
| Feature | Monero | Bitcoin |
| Privacy | Transactions are completely private and untraceable | Transactions are traceable and publicly visible |
| Block size | Flexible block size to avoid congestion | Fixed block size with potential for higher fees |
| Mining | Uses regular CPUs for mining | Requires specialized ASICs |
| Fungibility | All coins are indistinguishable and fully fungible | Coins can be tainted by previous transactions |
| Anonymity | Automatic anonymity for all users | Pseudonymous, but not anonymous |
| Supply limit | No hard supply limit; continuous emission through tail emission | Hard supply limit of 21 million BTC |
| Transaction speed | Transactions are generally faster due to flexible block size | Transactions can be slower during high congestion |
| Governance | Community-driven with off-chain governance | Open-source development with community consensus |
| Regulatory scrutiny | Higher due to privacy features | Lower due to traceability and transparency |
Monero crypto (XMR)
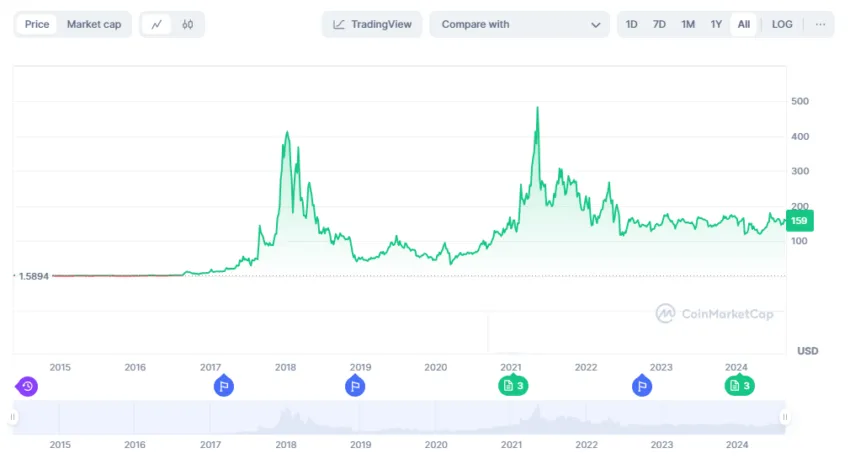
$XMR is used as a native currency within the Monero network. As of Aug. 27, 2024, the Monero crypto ranks 29th in the global crypto ratings with a market cap of just over $2.9 billion.
You can use XMR for peer-to-peer payments and value storage within the Monero network. The native coin also covers transaction fees.
Due to its powerful privacy features, offering anonymity by default, $XMR has found significant usage as a black or grey market currency.
Our Monero price prediction puts the potential future price of XMR at a maximum of $232 in 2025, $255 in 2026, and $281 in 2027.
Note that crypto price predictions can never be completely accurate and should only be used as a guideline. While fundamental and technical analysis can provide solid groundwork, news cycles, wider market forces, and social sentiment can all impact the price of a crypto, XMR included.
If you are looking to buy Monero, you can do so on several leading crypto exchanges, including OKX (best for spot and copy trading), Kraken (best for security features), and Binance (most comprehensive overall ecosystem).
XMR tokenomics
Similar to Bitcoin and Litecoin, Monero block rewards decrease over time. Monero (XMR) operates via a set of tokenomics characterized by a focus on privacy and limited inflation.
Monero has a block reward of 0.6 XMR, translating to approximately 0.3 XMR generated every minute. This relatively low inflation rate results in roughly $80 of new XMR entering circulation each minute.
Monero’s emission rate was carefully designed to ensure fair coin distribution as the network evolved. The emission rate was relatively high in its early days and gradually decreased as the network matured.
This approach encouraged early adopters, such as miners, while also preventing a sudden flood of XMR coins into the market, which could have threatened its intrinsic value.
Governance
Monero’s governance happens off-chain, with improvement proposals submitted on GitHub and subject to community voting. Upon consensus and approval, the code is integrated into the Monero Core Client, though node updates can be slow due to the decentralized nature.
Monero schedules biannual hard crypto forks to address this, encouraging node operators to stay engaged and ensuring timely updates. The most recent hard fork occurred on July 16, 2022.
Monero’s path forward
Monero is the most important and well-known privacy coin. The network provides a crucial service by empowering individuals to protect their financial privacy and retain control over their assets. However, Monero’s future is not guaranteed. Some consider it too obscure for institutional investors.
Meanwhile, its privacy features are a concern to governments; the currency has the potential to facilitate the bypassing of restrictions and sanctions. This resistance to government control benefits Monero users but will likely hinder broader adoption and leave the network and XMR currency vulnerable to regulatory woes.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice. Proceed with caution if you plan to buy Monero (XMR).
Frequently asked questions
What is Monero?
Is Monero crypto a good investment?
Is Monero better than Ethereum?
Is Monero risky?
Can Monero transactions be traced?
When was Monero launched?
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, the educational content on this website is offered in good faith and for general information purposes only. BeInCrypto prioritizes providing high-quality information, taking the time to research and create informative content for readers. While partners may reward the company with commissions for placements in articles, these commissions do not influence the unbiased, honest, and helpful content creation process. Any action taken by the reader based on this information is strictly at their own risk. Please note that our Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers have been updated.