High fees and limited scalability are common problems among many blockchain platforms. EOS promises a solution to this challenge with its fee-less transactions, scalable architecture, and user-friendly design. This article explores the EOS network, its key features, and the potential of the EOS crypto as an investment option in 2025.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
• EOS is a layer-1 blockchain built on the Antelope protocol. It is designed for scalability and security.
• EOS is popular for its fee-less transactions, user-friendly design, and advanced scalability features.
• The EOS crypto has versatile use cases, including value exchange, DeFi, NFTs, GameFi, and network governance.
What is EOS?
EOS operates as a layer-1 blockchain built on the open-source Antelope protocol (previously known as EOSIO). This protocol addresses critical concerns like scalability, security, and decentralization of blockchain applications.
Unlike Ethereum’s rental system, EOS directly allocates computational resources to coin holders, thereby eliminating the need for rent or gas fees.
EOS employs both vertical and horizontal scaling to offer fee-less applications. It aims to create a reliable platform that prioritizes user and business-friendly app development while mitigating the constraints found in other blockchain platforms like Ethereum.
History of EOS
Block.one, led by Dan Larimer and Brendan Blumer, kicked off the EOS project in August 2016. In April 2017, they launched the EOS GitHub repository, followed by a technical whitepaper detailing the project’s vision in June 2017.
EOS’s initial coin offering (ICO) started in June 2017 during an ICO boom that saw various blockchain initiatives rake in hefty capital. On July 1, 2017, Block.one announced that the ICO had raised a record-breaking $185 million in just five days.
By June 2018, the amount raised by the ICO stood at a staggering $4 billion, making EOS one of the most significant ICOs in history.
Despite the successful ICO, EOS faced a major controversy over how Block.one allocated and spent the funds. This situation led to concerns about transparency and accountability within the project.
The EOSIO version 1.0 was released in 2018, and the mainnet officially went live in the same year, with token holders playing a key role in its launch. In April 2023, the EOS Network Foundation launched its EOS EVM on the mainnet, facilitating interoperability between EOS and Ethereum.
How does EOS work?
EOS was primarily designed to solve the challenges developers face when building applications for large-scale blockchain networks. Some of the major aspects of its functionality include:
A WebAssembly C++ engine
EOS uses WebAssembly (Wasm) technology, which enables developers to create high-speed applications using popular programming languages such as C++. This allows for faster development and a more accessible learning curve for developers.
Scalability
Blockchain scalability can be a major concern due to consensus requirements for transaction processing. This requirement inevitably leads to slow performance.
For instance, Ethereum could originally handle only 20 transactions per second (tps), which is dwarfed by VISA’s 1667 tps. EOS addresses this issue using delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS), which can manage millions of transactions per second.
DPoS uses real-time voting and reputation mechanisms to select block producers, with EOS crypto holders participating. Each coin represents a vote that can be used for platform development support.
Delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS).
In DPoS, computers on the network do not compete over computational power through mining. Instead, network users vote for a set of computers best qualified to run the network. These are called block producers.
Additionally, DPoS offers faster and more energy-efficient solutions than PoW. Here’s how DPoS works on EOS:
- Block producers: In EOS, the 21 block producers who receive the most votes from users are delegated to run the network. These block producers are often professional teams operating enterprise-grade hardware.
- Transaction validation: Each block producer takes turns validating transactions and producing blocks, which are subsequently verified by the other 20 block producers.
- Reward system: The system rewards block producers with EOS crypto for upholding the network’s integrity and ensuring its smooth functioning.
- User oversight: EOSIO allows users to withdraw their votes from block producers who fail to uphold their responsibilities. Any such scenario can lead to the immediate replacement of an underperforming block producer.
Flexibility and security with EOS
EOS features a comprehensive permission system that allows developers to create tailored authorization schemes for different business scenarios.
Developers can protect specific smart contract features and distribute authority for contract functions across multiple accounts.
EOS lets developers upgrade apps and allows them to fix code and add features without protocol constraints.
Governance in EOS
EOS establishes governance through a legally binding constitution that appends to transaction signatures. The constitution also outlines jurisdiction, choice of law, and agreed-upon regulations, which ensures transparent governance.
What makes EOS unique?

Unlike Ethereum’s rental system, EOS directly allocates computational resources to coin holders. This approach eliminates the need for rent or gas fees.
Some of the network elements/characteristics that make it unique include:
- Scalability: EOSIO is built to scale efficiently, which allows applications to process transactions with significantly lower latency compared to other blockchains. Instead of waiting minutes or hours for transaction confirmations, EOSIO transactions take just half a second.
- Zero transaction fees: Unlike many other blockchains that charge transaction fees, EOS transactions are free. This means that users can send tokens, engage in microtransactions, or perform various actions without incurring additional costs.
- User-friendly: EOSIO focuses on ease of use for both developers and users. It offers free transactions for actions such as sending tokens, selling in-game items, and liking comments. These on-chain transactions are highly secure, and users can even choose short account names, making account management more straightforward.
- Unique security features: EOSIO introduced permissioned private keys, which are keys with limited capabilities. For example, a permissioned private key can post a message but cannot send tokens, enhancing the security of the ecosystem.
- Governance: EOS maintains governance through a legally binding constitution. The constitution establishes jurisdiction, choice of law, and mutually agreed-upon regulations. This system ensures a structured and regulated environment.
- EVM integration: It connects two prominent blockchain ecosystems, Ethereum and EOS. This mainnet replicates Ethereum’s Virtual Machine (EVM) to provide developers with the capability to launch DApps coded in Solidity.
The EOS crypto (EOS)
EOS crypto is the native coin of the EOS ecosystem, having transitioned from its initial launch on the Ethereum platform to the EOS network. This digital asset finds utility in various functions, including staking, governance, and facilitating economic transactions.
Notably, the EOS coin does not have a supply cap. Its annual inflation rate is 1% after a revision from the original 5% rate, which took effect in February 2020. EOS has a circulating supply of over 1.5 billion tokens and a maximum supply of 2.1 billion.
“EOS is certainly better off than it was two years ago. The market downturn on crypto has been rough for all Antelope chains but, the slip doesn’t mean I’m ready to sell all my EOS/Antelope coins to ape into whatever the popular meme tokens are for this week.”
@JeremyinKansas: Twitter
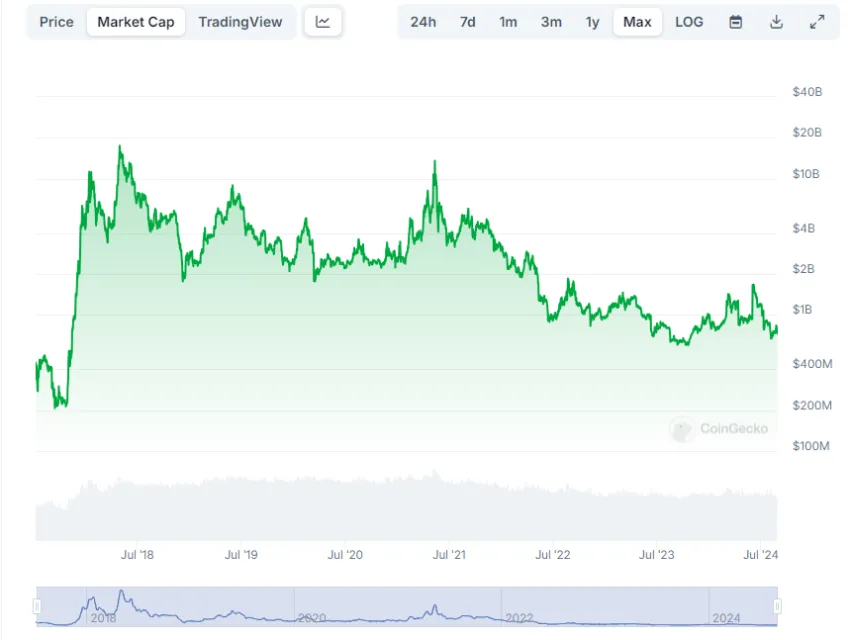
As of Aug. 29, 2024, EOS ranks as the 80th largest cryptocurrency with a market cap exceeding $737 million.
Token utility
- Value exchange: Serves as a global digital cryptocurrency, facilitating smooth value exchange within the EOS network’s diverse ecosystem.
- DeFi engagement: Enables users to participate in DeFi transactions, including lending, borrowing, and yield farming.
- NFT marketplace: Powers the buying and selling of verified digital art through NFTs.
- GameFi participation: Grants access to GameFi platforms, allowing users to engage in play-to-earn gaming and other value-generating activities.
- Governance and network resources: EOS holders enjoy governance privileges. They also use EOS to access network bandwidth and storage capacity for essential operations, such as transfers and interactions with DApps and smart contracts.

EOS price potential
Our EOS price prediction projects a potential value of $2.129 for EOS in 2023, rising to $3.086 in 2025 and reaching $10.04 by 2030. However, if you’re eying EOS as an investment, note that various conditional factors influence these predictions.
Never consider crypto price predictions as absolute certainties. The future EOS price will ultimately depend on the state of the market, layer-1 competition, and further adoption of EOS.
Is it worth buying EOS crypto?
EOS offers something novel. Its fast and fee-less transactions and efficient smart contracts pave the way for the develop-friendly blockchain to seamlessly facilitate secure, rapid, and cost-effective interactions across the globe. However, you should only consider buying EOS if you believe in the project. While the coin might have good long-term price potential, all crypto is a risky investment, and profits are not guaranteed, whether you choose to trade or HODL.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice. Crypto is volatile. Do your own research (DYOR) and never invest more than you can afford to lose.
Frequently asked questions
What is delegated-proof-of-stake (DPoS)?
Can I stake EOS for rewards?
Is EOS better than Ethereum?
Is EOS an “Ethereum killer?”
Does EOS have a future?
What is the advantage of EOS?
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, the educational content on this website is offered in good faith and for general information purposes only. BeInCrypto prioritizes providing high-quality information, taking the time to research and create informative content for readers. While partners may reward the company with commissions for placements in articles, these commissions do not influence the unbiased, honest, and helpful content creation process. Any action taken by the reader based on this information is strictly at their own risk. Please note that our Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers have been updated.




