Scalability is a key challenge that the Ethereum community is actively trying to solve. Ensuring limitless scalability is the only way to ensure mass adoption of the technology. And one of the most viable solutions to scalability that has emerged is Zero-Knowledge Ethereum Virtual Machines (zkEVMs).
This guide explains the fundamentals of zkEVMs and delves into the reasons zkEVMs are pivotal for scaling web3 and facilitating its widespread adoption. Lastly, we look at some use cases of this exciting new technology.
What are zkEVMs?
Before we understand zkEVMs, let’s familiarize ourselves with zero-knowledge proofs (ZKP), a key concept that forms the basis of zk tech. Essentially, a ZKP is a cryptographic proof allowing one party to prove to another party that they possess certain information without revealing it.
There are several algorithms available today to generate ZKPs. The two most compelling are zk-STARKs and zk-SNARKs. Both are acronyms for the method by which the two parties prove their knowledge: zk-STARK stands for the zero-knowledge scalable transparent argument of knowledge. Meanwhile, zk-SNARK stands for the zero-knowledge succinct non-interactive argument of knowledge.
Now let’s understand what a zkEVM is. A zkEVM is a zk-rollup that mimics Ethereum’s transaction execution environment and executes smart contracts. It proves the correctness of execution using ZKPs. ZkEVMs recreate aspects of Ethereum’s design and thus provide an “Ethereum-like” experience for developers and users. When combined with rollup technology, a zkEVM provides unparalleled security and scalability for decentralized applications (DApps) and their users.
A zk-rollup reduces Ethereum’s computational loads by executing transactions in a separate layer-2 (L2) environment. The rollups operator called a sequencer, periodically bundles transactions on the L2 into a rollup batch and submits proof of this to a smart contract on layer-1 (L1) Ethereum.
Why do we need to scale Ethereum?

The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is a distributed computing environment that runs on the Ethereum network. It is crucial to the network as it allows for the execution of smart contracts and powers the various DApps that operate on Ethereum.
As more users have gravitated towards Ethereum, network limitations have led to high gas prices or the fee a user pays to use the network. As a result, the Ethereum network provides the benefits of security and decentralization but trades scalability in the process, as every node on the network needs to re-execute transactions and store the world state.
Some solutions that have emerged to address Ethereum’s scalability issues are sidechains and rollups. Sidechains act like independent blockchains running parallel to L1 Ethereum. Meanwhile, rollups execute transactions offchain, bundle them, and post them to the L1. A criticism of these solutions remains that they do not scale Ethereum directly. However, they allow developers to run Ethereum DApps on an off-chain layer that is scalable while being a low-cost option for users.
Not all scaling solutions are created equal. Take, for instance, the case of sidechains, which lack the security provided by the Ethereum network. Consequently, the safety of users’ funds hinges on the integrity of the validators associated with the sidechain. In a dire situation, if the validator set becomes compromised, there is a significant risk of funds being illicitly appropriated from a bridge or users being denied access to legitimately owned funds through transaction censorship.
Zk-rollups have quickly become one of the most effective ways to solve Ethereum’s scalability issues. Since they are “zero-knowledge,” they only need validity proof, not the entire transaction’s data. This ensures zk-rollups need less block space, making the verification process quicker and cheaper than executing the transaction on an L1.
What are some zkEVM Projects in the Ecosystem?
A number of L2 projects have emerged in the Ethereum ecosystem over the past couple of years. However, we will focus on the four most notable.
zkSync Era

ZkSync Era, developed by Matter Labs, is an EVM-compatible zkVM supporting general-purpose applications. It is an upgrade to zkSync Lite and provides low-fee ERC-20 token and ETH transfers, swaps, and NFT minting/trading.
ZkSync Era adopts a compiler-based approach for EVM compatibility — it uses a special compiler to convert the high-level programming language, such as Solidity or Vyper, into a format suitable for the zkSync zkEVM. This change leads to some incompatibility with Ethereum but offers benefits like improved proof generation times and lower costs for end-users.
ZkSync Era opened on the Ethereum mainnet to all users on March 24, 2023.
StarkWare
StarkWare is the developer of two distinct zk products: StarkEx, a permissioned scaling service powering applications like dYdX, Sorare, ImmutableX, and rhino.fi, and StarkNet, a general-purpose rollup tailored for executing Cairo programming language applications.
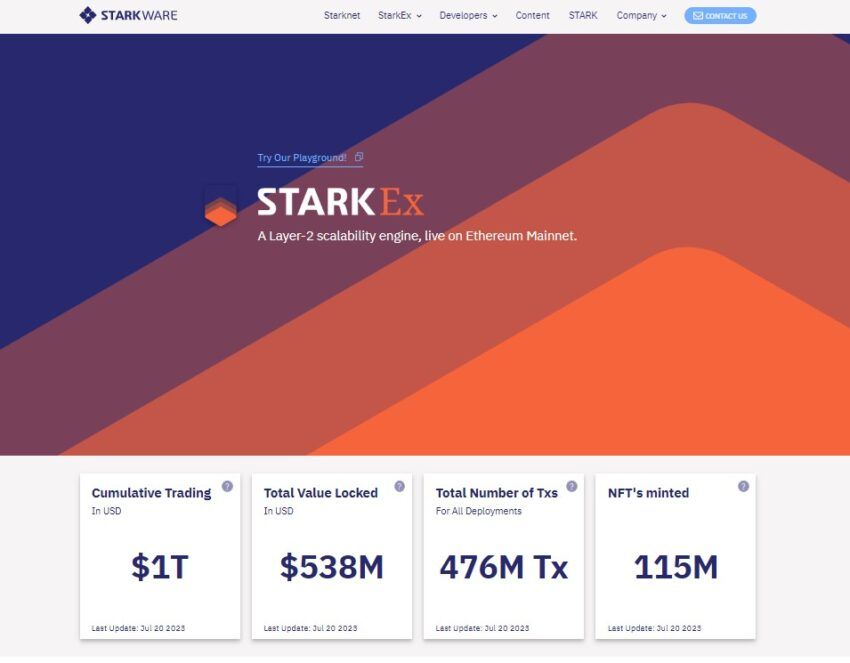
Notably, StarkWare is credited with popularizing “validiums,” which function as rollup-like structures with off-chain data availability. By ensuring correctness through validity proofs, validiums offer superior security compared to other scaling solutions with off-chain data availability.
StarkNet launched on Ethereum mainnet on April 25, 2023.
Polygon zkEVM

Polygon zkEVM positions itself as an “EVM-equivalent zkEVM.” Essentially, this is a zkVM that can understand and process the same instructions as the Ethereum Virtual Machine.
STARKs are used for generating proofs of computational integrity in the Polygon zkEVM, although a SNARK (generated using PLONK) is used for L1 verification purposes. This combination provides a “best of both worlds” scenario wherein STARK is used to generate proofs quickly. Meanwhile, a final SNARK proof that attests to the correctness of the STARK proof is used to reduce verification costs.
Polygon zkEVM debuted on the Ethereum mainnet on March 27, 2023.
Linea

Linea is a developer-friendly Type-2 zkEVM. The research and development team at Consensys developed the rollup. It is an EVM-equivalent zk-rollup solution that is fully compatible with existing tooling and infrastructure. This allows developers to develop as if they were doing so on Ethereum mainnet (Linea uses ETH for gas payments, for example) at a fraction of the cost of building on Ethereum.
As a Type 2 zkEVM, Linea prioritizes compatibility with all Ethereum applications and infrastructure above everything else. It allows for seamless integration with EVM wallets (MetaMask). Plus, developer tooling (Truffle, Remix, Brownie, Foundry, Hardhat, et al.) and critical infrastructure like node providers (Infura) and execution clients (Besu).
Linea offers the benefits of being an Ethereum scaling solution — low fees, fast confirmations, and a high number of transactions per second — while avoiding the downsides some of the competing projects may have. For example, delayed finality, high costs, and poor security.
In addition, Linea provides an EVM-equivalent infrastructure. This means users can build new DApps while benefiting from Ethereum’s security, decentralization, and developer experience.
Linea’s launch on the Ethereum mainnet was announced on July 11, 2023, and it began to onboard partners that same day. It opened the network to all users on July 18th, 2023.
What are the applications of zkEVMs?
DeFi: Traders and investors stand to benefit from enhanced capital efficiency and improved liquidity access with minimal withdrawal delays on a zkEVM rollup. The exponential growth in cost savings within the DeFi space on a zkEVM is particularly noteworthy. This is because there is no need to compensate liquidity providers for expedited exits.
In addition, the optimization of a zkEVM for scalability translates to blazingly fast and cost-effective decentralized computer operations. This makes it an ideal choice for peer-to-peer payments and institutional settlements. Ethereum’s highly decentralized network, with over 500,000 validators and continuing growth, ensures robust transaction finality guarantees.
Gaming: On-chain gaming applications that handle a significant volume of transactions greatly benefit from the scalability advantages offered by zkEVMs. In addition to the previously mentioned benefits, on-chain gamers enjoy reduced costs per transaction. This is due to the data compression capabilities inherent in zkEVMs.
NFTs: The exceptional combination of ultra-low gas fees and high transactions per second on a zkEVM chain makes it an ideal platform for large-scale NFT minting and trading. Furthermore, the seamless user experience of transferring NFTs to Ethereum L1 is ensured by the immediate finalization of withdrawals once the on-chain verifier contract accepts the submitted proof.
Social media: Another area where zkEVMs are proving useful is social media. Take a DApp such as Lineaster, a decentralized social media platform that is built by Lens Protocol and deployed on Linea. Lineaster is able to leverage the high throughput and low gas fees enabled by Linea.
Multi-prover zkEVMs are the future
In all, it’s clear the potential of zkEVMs in the proliferation and adoption of web3 is unmatched. But in particular, multi-provers have a special role to play. In the case of a multi-prover zkEVM, each transaction posted to an L2 is proved by multiple independent provers. That is, one batch of transactions could have many validity proofs confirming the integrity of the transaction data contained in that batch.
To make this possible, we need multiple Type-2 EVM equivalent zkEVMs that are performant and can collaborate with each other. There are many benefits of a multi-prover zkEVM. A key one is that it reduces the risk of failure, as there is no single point of attack. Another benefit is that it encourages innovation in prover schemes.
Vitalik Buterin refers to most rollup solutions available today as being on “training wheels,” meaning that a project still relies on multi-sig to ensure a particular outcome in the case of bugs in the code. They do not yet rely fully on the Zk-proof tech. Yet the multi-prover solution is key to helping remove these “training wheels” and allowing the benefits of this tech to truly be realized.
Frequently asked questions
What is a zkEVM?
Why are zkEVMs important for Ethereum scalability?
About the author

Simran Jagdev is a senior content manager with Consensys, a leading blockchain and web3 software company. A tech-focused writer and business journalist, Jagdev has been in the web3 ecosystem since 2021. Her work mostly focuses on institutional engagement with web3, Ethereum’s burgeoning layer-2 scene, and developments in the overall Ethereum ecosystem. She is most excited about web3’s ability to build meaningful communities around shared interests.
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, the educational content on this website is offered in good faith and for general information purposes only. BeInCrypto prioritizes providing high-quality information, taking the time to research and create informative content for readers. While partners may reward the company with commissions for placements in articles, these commissions do not influence the unbiased, honest, and helpful content creation process. Any action taken by the reader based on this information is strictly at their own risk. Please note that our Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers have been updated.




