Since its launch, Ethereum has undergone several network upgrades to address scalability, efficiency, and security. These upgrades are usually hard forks that focus on specific parts of the blockchain. The Ethereum Cancun-Deneb Upgrade, also known as Dencun, is an upgrade that made significant changes to the world’s second-largest blockchain.
Dencun marked a significant milestone for the network, improving throughput and reducing transaction costs, benefiting the network’s growing number of layer-2 chains. Read on to learn more about this major upgrade and its impact on Ethereum’s future.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
► The Ethereum Cancun-Deneb (Dencun) upgrade focused on enhancing scalability, efficiency, and reducing transaction costs through proto-danksharding.
► Key Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) introduced with Dencun aim optimized data storage, reduced gas fees, and improved security within the network.
► While Dencun lowered operating expenses for layer-2 rollups, it also decreased their total revenue, yet increased their profit margins.
► The Dencun upgrade strengthens Ethereum’s infrastructure for future developments but may reduce Ethereum’s security by diverting fees to layer-2 networks.
What is the Ethereum Cancun-Deneb (Dencun) upgrade?

Dencun is an Ethereum upgrade that improved the blockchain’s scalability through Proto-Danksharding. The combination of the Cancun and Deneb upgrades also focused on boosting the Ethereum network’s efficiency and security.
The Cancun and Dencun upgrades complemented each other to complete Dencun. While Cancun upgraded Ethereum’s execution layer, Deneb addressed the consensus layer.
Besides Proto-danksharding, the Cancun-Deneb (Dencun) update also comprised several critical Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs), all geared towards improving the network.
With the Dencun upgrade, the primary emphasis was optimizing Ethereum’s execution layer. Doing so laid the groundwork for implementing full data sharding in the network as part of Ethereum’s long-term technical development strategy.
Ethereum co-founder noted that with the Dencun upgrade, the network will concentrate on eliminating scalability bottlenecks. Ethereum founder Vitalik predicted these types of scaling improvements as far back as 2020.
Look forward to the future of Ethereum scaling!
(Including sharding supercharging all of these techniques 100x further down the line)
Vitalik Buterin: X (2020)
This upgrade marks the initialization of “The Surge phase” in the Ethereum blockchain tiered roadmap. The goal is to boost performance and attain mass adoption via layer-two rollups without hampering decentralization.
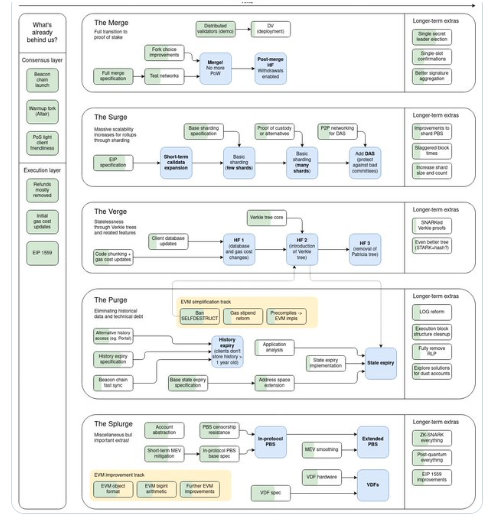
The Dencun upgrade ran on the Goerli testnet on Jan. 17, 2024, transitioned to the Sepolia test net on Jan. 31, 2024, and went live on Mar. 13, 2024.
Ethereum Dencun EIPs explained
Ethereum improvement proposals, or EIPs, are a series of recommended updates within the Ethereum upgrade. The proposals lay emphasis on enhanced blockchain scalability, increased efficiency, and improved security within the Ethereum blockchain. Below are the EIPs.
- EIP-1153: The proposed change seeks to optimize data storage within the Ethereum ecosystem. It introduces 2 EVM codes designed to make gas fees more economical. These opcodes are set to self-erase at the end of each transaction.
- EIP-4788: Exposes Ethereum’s Beacon chain data to the execution layer by storing them in a smart contract. It aims to bolster the network architecture and improve security and functionality.
- EIP-4844: Proto-danksharding ushers in temporary data blobs for rollup usage, facilitating more affordable transactions.
- EIP-5656: Adds MCOPY, allowing for a simpler and less costly way to copy memory in the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) for better performance.
- EIP-6780: Updates the SELFDESTRUCT code, limiting the termination of smart contracts via the code while enhancing user data protection and securing funds.
- EIP-7044: Eliminates restrictions placed on the credibility of a validator’s exit message.
- EIP-7045: Increases the time in which an attestation can be included as part of a Beacon Chain block.
- EIP-7514: Limits on the number of validators to be activated during an epoch.
- EIP-7516: Introduces BLOBBASEFEE opcode, which returns the value of the blob base fee of the block undergoing execution.
What is EIP4844 and Proto-danksharding?
EIP-4844, otherwise referred to as Proto-danksharding, is among the EIPs in the Ethereum Cancun-Deneb upgrade. Ethereum users pay lower transaction fees on Ethereum layer-2 (L2) transactions as a result of danksharding.
The Ethereum network has undergone several upgrades over the years to maximize its capacity. Examples include the Gray Glacier upgrade and the Shanghai upgrade. Developers have been keen to provide an effective solution to the twin challenges of high gas fees and transactions throughout.
Enter sharding — a method of dividing databases into smaller sizes to manage particular data segments, thus boosting performance. However, this proposed long-term solution is lengthy and complex. Proto-danksharding offers a better solution.
The proposed amendment to the Ethereum network significantly lowers transaction fees and increases throughput. As a prototype of danksharding, proto-danksharding is a temporary fix to be employed before the full implementation of danksharding in the future.
Danksharding and proto-danksharding are both critical elements in the Ethereum consensus layer upgrade and the overarching mission to optimize Ethereum’s full potential.
Danksharding refers to a type of sharding that occurs in the last phase of the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade. It emphasizes optimizing data availability and management within the Ethereum system by improving transaction processing and streamlining data storage. It also ushers in an innovative concept — a merged market fee.
To achieve Proto-danksharding, a transitional step in the danksharding strategy, a new transaction type with unique capabilities was introduced — one that accepts data blobs. Essentially, EIP4844 attaches blobs onto transaction blocks. Ethereum expects to scale dramatically, increasing its TPS to approximately 100,000 through danksharding.
As mentioned previously, the Cancun upgrade will concentrate on optimizing the execution layer (layer-1). This will form the basis for the eventual implementation of full data sharding, as per Ethereum’s long-term developmental strategy.
Sharding entails dividing a blockchain database into smaller shards. The goal is to boost overall efficiency. With the Cancun upgrade, it takes on a new form, i.e., proto-danksharding.
The importance of Proto-danksharding
As discussed earlier, proto-danksharding is a major step towards maximizing operations, optimizing data management, and reducing transaction costs within the Ethereum ecosystem.
Proto-danksharding presents a viable solution to the Ethereum blockchain trilemma – security, decentralization, and scalability. The trio hampers Ethereum’s ability to run efficiently at lower costs.
Proto-danksharding is a vital aspect in upgrading the Ethereum consensus layer and promises to elevate Ethereum’s proficiency and scalability. It introduces temporary storage space, enabling users to load data to blobs that attach to transaction blocks – at a reduced cost.
Also, the data gets expunged after a fixed period, saving space and reducing transaction costs. Consequently, this allows layer 2 rollups to achieve higher transaction volumes cost-effectively.
As an integral component of EIP-4844, proto-danksharding is a core element in the future of Ethereum scaling endeavors. Additionally, it is now officially incorporated into EIPs within the Ethereum Cancun upgrade.
Pros and cons of the Cancun upgrade
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Improved security | Smart contract risks |
| Elevated scalability | Upgrade could hurt ongoing processes |
| Better data-availability and storage | |
| Lower operational costs |
Benefits of Ethereum Cancun
Ethereum Cancun promises many benefits not only to Ethereum’s growing user base but also to developers. These include:
- Improved security: The update promised a more secure and user-friendly experience. It revolutionized transaction processing and protected user data.
- Improved cross-chain communication: The upgrade enabled easier, safer, and more seamless interactions between different networks and supported interaction with Layer 2 solutions.
- Elevated scalability: The proposed amendments tackled scalability constraints, significantly raising transaction volumes within the Ethereum network per second.
- Better data availability and storage: The update sought to optimize Ethereum’s data storage and reduce storage fees, thereby improving efficiency.
- Lower operational costs: The update aimed to lower gas fees per transaction on the Ethereum blockchain via blob-carrying transactions.
- Increased speed of Ethereum’s transaction per second (TPS). This move was expected to facilitate faster and increased traffic on the Ethereum network.
- Encourage technical Innovations: The Dencun upgrade laid the foundation for future technological developments, paving the way for enhanced operations and raising Ethereum’s competitive edge.
Risks of Ethereum Cancun
Like previous upgrades, the Dencun upgrade carried some risks. Here are some of them.
- Impact on current smart contracts: Introducing new features and changes, such as innovative data storage techniques, could lead to compatibility issues in existing smart contracts.
- Integration: While the Ethereum Cancun upgrade aimed to enhance data storage proficiency, data migration might not be a seamless affair. This could have negatively impacted ongoing operations. Hence, proper planning and information sharing before execution was key.
Ethereum’s Dencun upgrade and its impact
Ethereum’s Dencun upgrade had a huge impact on Ethereum. For starters, it dramatically lowered the fees paid to Ethereum, impacting security. This is because much of the fees that Ethereum validators collected came from layer-2s.
For context, Ethereum is structured so that the more activity (transactions), the more ETH is burned. Every Ethereum transaction burns a portion of the transaction fee (called the base fee). With high amounts of activity, ETH becomes net deflationary.
Furthermore, the cost of operating a layer-2 has dropped, along with the revenue collected by layer-2 operators. To put it simply, Ethereum layer-2s must pay fees to operate on Ethereum. Operators on layer-2s (which secure the network similar to an Ethereum validator) collect fees for processing transactions on rollups.
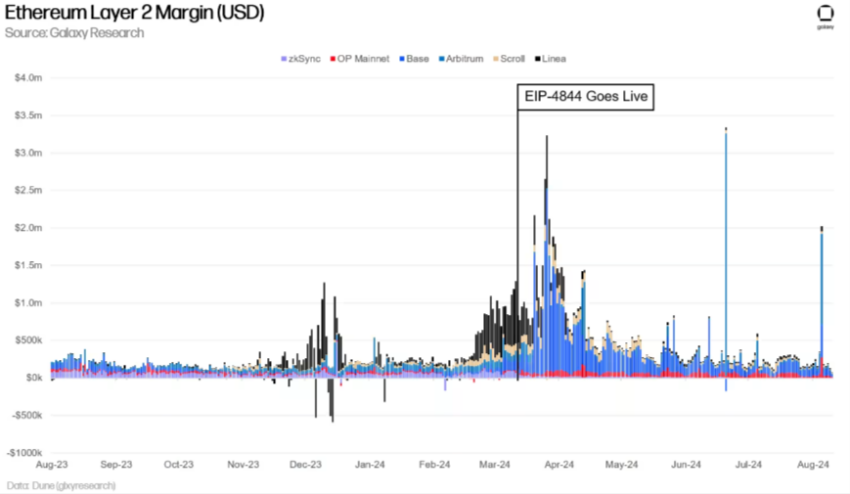
In other words, they collect fees from layer-2 users and pay fees to Ethereum to include the bundle of transactions.
However, while the total revenue and operating expenses declined, the margins increased. For example, if you own a store, the cost to create a product is $80, and you can sell the product for $100, then the margin is $20. If the cost to create the product decreases by $30, then your margin (gross profit) is $50, which increases by 150%. So, while your total revenue did not increase, your gross profit did.
Margin typically is the difference between the cost of producing or purchasing a product and the price at which it is sold.
To tie it all together, the product you are selling is processing layer-2 transactions, and your operating expenses are the costs to post transactions and data to Ethereum. Dencun lowered the operating expenses for rollups, which allowed them to offer lower fees and simultaneously decreased their total revenue; however, it also increased layer-2 profit margins.
Can the Dencun upgrade fortify the Ethereum ecosystem?
Ethereum Cancun-Deneb’s modifications address scalability, efficiency, and security, with the main thrust being lower transaction fees and an elevated Ethereum throughout. Ultimately, the upgrade has helped to fortify the Ethereum ecosystem and lay the foundation for the blockchain’s future development strategy.
However, the upgrade has also led to a siphoning of Ethereum users and fees, increasing profits for layer-2s and lowering Ethereum’s security. Undoubtedly, the Dencun upgrade will also cement Ethereum’s status as a frontrunner in innovations within the digital asset space and a key player in decentralized applications. Still, the long-term cost may be the rising dominance of layer-2’s.
Frequently asked questions
What is the Cancun update?
What is Dencun?
What is EIP 4844?
What is the ETH 2.0 update?
Will Ethereum 2.0 be a new coin?
How long will the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade take?
Will EIP-4844 reduce gas fees?
What is the ETH EIP-4844 upgrade?
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, the educational content on this website is offered in good faith and for general information purposes only. BeInCrypto prioritizes providing high-quality information, taking the time to research and create informative content for readers. While partners may reward the company with commissions for placements in articles, these commissions do not influence the unbiased, honest, and helpful content creation process. Any action taken by the reader based on this information is strictly at their own risk. Please note that our Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers have been updated.