Since Satoshi Nakamoto introduced the original blockchain — Bitcoin — the decentralized technology has quickly spread across industries. From facilitating the rethinking of financial systems to transforming healthcare and supply chain management, blockchain can reshape how we conduct transactions and share data. This article explores the fundamentals of blockchain technology, how it works, the challenges it faces, and its use cases in various walks of life. Here’s what to know in 2024.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
➤ Blockchain technology offers a decentralized, secure, and transparent way to record and verify transactions without intermediaries.
➤ Blockchain applications span multiple industries, including finance, healthcare, real estate, and supply chain management.
➤ Key challenges for blockchain adoption include scalability, regulatory uncertainty, and energy consumption in certain networks.
What is a blockchain?

Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that stores data across a distributed network. It is designed to secure information and prevent tampering and unauthorized access.
Each “block” in the chain contains data, which is verified, encrypted, and linked to the previous block, creating a chronological chain of data that is virtually immutable. This approach ensures data integrity, as altering any block would require changing every subsequent block, which is computationally impractical in most cases.
A blockchain typically operates across multiple computers or nodes and allows information to be shared without a central authority.
Blockchains are known for their role in enabling cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, but their use extends far beyond digital currencies.
They provide a transparent, secure, and decentralized method of recording transactions or data, which makes them applicable across various industries, such as finance, supply chains, healthcare, and governance.
“The blockchain does one thing: It replaces third-party trust with mathematical proof that something happened.”
– Adam Draper, co-founder at Boost VC
Understanding the basics
At the heart of blockchain technology are fundamental principles that distinguish it from traditional systems. These include decentralization, transparency, the use of a distributed ledger, and more.
What is a ledger?
A ledger is a record-keeping system for tracking transactions and ownership. Historically, ledgers were physical books or digital records maintained by a central authority, such as a bank.
A blockchain, however, uses a decentralized ledger where transactions are distributed across multiple nodes, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing trust.
Traditional ledgers vs. digital ledgers
Traditional ledgers depend on centralized authorities, like banks or corporations, to maintain and validate transaction records.
Digital ledgers, especially blockchains, distribute record-keeping across a network of computers. This makes it harder to tamper with the data and eliminates single points of failure, enhancing security and reliability.
The role of ledgers in record-keeping
Ledgers, whether traditional or digital, serve to document the flow of assets, information, or financial transactions.
Blockchain technology improves on this by creating an immutable and transparent record of each transaction. Once data is added, it cannot be altered, which ensures accuracy and integrity in record-keeping.
Decentralization: the core concept
Decentralization means distributing control and decision-making across a network rather than relying on a single central authority.
In blockchain, decentralization prevents any single entity from controlling the entire network. This distribution of power is crucial for making the network secure and resistant to manipulation or corruption.
Centralized vs. decentralized systems
Here’s how decentralized systems stack up against their centralized counterparts.
| Feature | Centralized system | Decentralized system |
| Control | A single entity or organization controls the system. | Control is distributed across multiple nodes. |
| Single point of failure | Yes, prone to failure if the central entity is compromised. | No, the network remains functional even if some nodes fail. |
| Security | Vulnerable to attacks if the central authority is compromised. | More secure due to the distribution of control and cryptography. |
| Transparency | Limited transparency, controlled by the central authority. | High transparency, as all participants can verify data. |
| Scalability | Generally easier to scale due to centralized control. | Scalability can be challenging due to consensus mechanisms. |
| Speed | Typically faster, as decisions are made centrally. | Can be slower due to the need for consensus among multiple nodes. |
| Trust | Requires trust in a single central authority. | Trust is distributed across the network; no single point of trust is required. |
| Costs | May incur higher costs due to intermediaries. | Can reduce costs by eliminating the need for intermediaries. |
| Resilience | Less resilient; failure or compromise of the central entity disrupts the system. | Highly resilient; distributed nature prevents single-point failure. |
Benefits of decentralization in blockchain
Decentralization ensures that no single point of control exists, which reduces the risk of corruption and censorship. It also enhances transparency, as all participants can verify the integrity of the network.
Additionally, decentralization increases the resilience of the system, as the network can continue functioning even if some nodes are compromised.
Hashing and cryptography
Hashing involves using a mathematical function to convert input data into a fixed-length string, called a hash. Blockchain uses hashing to secure data within each block.
Any small change in a block’s data results in a completely different hash, making any data tampering easily detectable.
Cryptography for security and privacy
Blockchain relies on cryptographic techniques to protect user identities and ensure the integrity of transactions. Public-key cryptography allows users to sign transactions with their private keys, so only authorized participants can modify the data.
Immutability and transparency
Immutability refers to the inability to alter or delete data once it has been added to the blockchain. This feature enhances trust, as all participants know that the data is permanent.
Blockchains also offer transparency, as the entire transaction history is available for anyone to view and verify, creating accountability.
Open access to transaction history
Blockchain networks provide an open and auditable ledger. Any participant can view the entire transaction history, which enhances trust and transparency.
This level of openness is particularly useful in industries where accountability and verification are essential, such as supply chains or voting systems.
Consensus mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms are protocols that ensure all nodes in a blockchain network agree on the validity of transactions. They allow decentralized networks to function without a central authority, ensuring consistency and trust across the system.
Proof-of-work (PoW) and proof-of-stake (PoS) are two of the most popular and commonly used consensus mechanisms.
- Proof-of-work (PoW): Proof-of-work requires participants to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add new blocks. This process, known as mining, consumes significant computational power. PoW is secure but highly energy-intensive, making it less efficient for large-scale applications.
- Proof-of-stake (PoS): Proof-of-stake allows validators to create new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold. Instead of competing to solve puzzles, validators are chosen at random, reducing energy consumption and increasing efficiency. PoS offers a more sustainable alternative to PoW.
Keen to learn more about the distinction between proof-of-work and proof-of-stake? Check our comprehensive comparison here.
Many major blockchain networks, including Bitcoin, use PoW. Meanwhile, Ethereum, which initially relied on PoW, transitioned to PoS in 2022 with the Ethereum Merge. The transition significantly improved its energy efficiency and scalability.
Other consensus mechanisms
While PoW and PoS are among the most popular consensus mechanisms, several other alternatives are gaining popularity as well. A few of them are:
- Delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS): It uses a voting system where participants elect a small group of trusted validators to confirm transactions, improving scalability.
- Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT): This mechanism relies on participants reaching a consensus through a voting process to ensure fault tolerance and efficiency. It is commonly used in private and consortium blockchains.
- Proof-of-authority (PoA): PoA grants transaction validation rights to a few authorized nodes only. It is a suitable option for private networks where trust between participants is established.
- Proof-of-burn (PoB): Validators “burn” or destroy cryptocurrency to demonstrate commitment and gain the right to mine or validate transactions.
How does a blockchain work?
As the name suggests, a blockchain consists of blocks that store data. Each block includes:
- Transaction data: This can range from financial transactions to records of goods in a supply chain.
- Hash: A unique string of characters generated by a cryptographic algorithm based on the data inside the block.
- Previous block hash: This links each block to the one before it and forms a chain that maintains the chronological order of all data.
- Timestamp: The exact time the block was created and added to the blockchain.
These blocks are linked together through cryptographic techniques, which makes them immutable. Once data is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered without changing every subsequent block, which would require immense computational power.
For instance, if a malicious actor attempts to change any data in a block, the hash of that block will change. Since every block contains the hash of the previous block, this modification would break the chain and the entire network will be alerted about the attack.
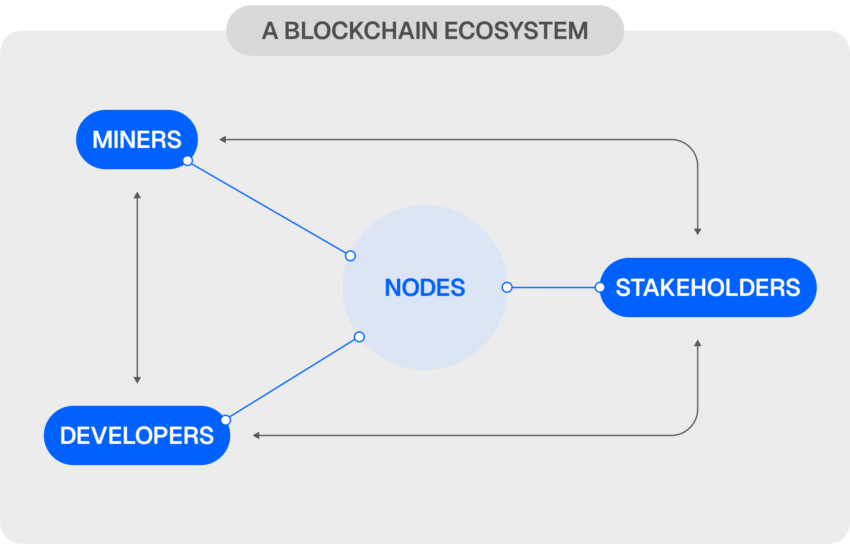
A blockchain ecosystem includes several key components that work together to maintain the network:
- Nodes: These are the participants responsible for verifying and validating transactions. They store copies of the distributed ledger and ensure consistency across the network.
- Miners: In proof-of-work systems, miners validate transactions and create new blocks by solving cryptographic puzzles. They are rewarded for their efforts with cryptocurrency.
- Stakeholders: These participants hold tokens or cryptocurrency within the network. They can play a role in governance, especially in proof-of-stake systems, by validating transactions and securing the network.
- Developers: They design and maintain the blockchain infrastructure. Developers are responsible for writing the code that powers the network and implementing features like smart contracts and protocols.
These components work together to maintain the decentralized, secure, and transparent nature of blockchain networks.
Types of blockchains
Blockchain networks can be categorized based on how they manage access, governance, and data transparency. Different types of blockchains offer various levels of decentralization, security, and efficiency, each suited for specific use cases and industry needs. Below are the four primary types of blockchains, each with unique characteristics and applications.
1. Public blockchains
Public blockchains are open to anyone who wishes to participate. These blockchains, such as Bitcoin, offer transparency and decentralization but typically require more resources to maintain their security.
Anyone can validate transactions and create new blocks, which makes these networks highly secure but somewhat slower.
2. Private blockchains
Private blockchains restrict access to a select group of participants. Organizations control these networks, which makes them more efficient for specific enterprise use cases.
Private blockchains allow for higher transaction throughput and lower costs but sacrifice decentralization and transparency.
3. Consortium blockchains
Consortium blockchains are governed by a group of organizations rather than a single entity. These networks offer a balance between public and private blockchains — they provide the security and scalability of private networks while maintaining some decentralization.
This model is particularly suited to industries like banking, where multiple entities must collaborate on transactions.
4. Hybrid blockchains
Hybrid blockchains combine elements of public and private blockchains. Some parts of the blockchain are open and accessible to the public, while others are restricted to a select group of participants.
This structure enables organizations to control sensitive data while still benefiting from the transparency and security of a public blockchain.
Hybrid blockchains are particularly useful in industries where data privacy is critical, but certain operations must remain transparent, such as in real estate or regulatory compliance.
Blockchain applications

“Instead of putting the taxi driver out of a job, blockchain puts Uber out of a job and lets the taxi driver work with the customer directly.”
– Vitalik Buterin, co-founder of Ethereum
Healthcare
Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLTs) like blockchain can store medical records securely, ensuring data integrity and privacy. Patients can control access to their health data and share it with healthcare providers without the risk of tampering or unauthorized access.
Blockchain can also improve the interoperability of medical records across different institutions.
Example: MediBloc, a blockchain-based healthcare platform, allows patients to manage and share their medical records securely, improving data interoperability across different healthcare providers.
Supply chain management
Blockchain enhances supply chain transparency by tracking products at each stage of the journey, from production to delivery. It ensures that all stakeholders can access accurate information about the origin, quality, and handling of goods.
Example: Walmart uses IBM’s Food Trust blockchain to track the origins of food products, ensuring faster identification of contamination sources and improving food safety.
Government
Governments can use blockchain to streamline services such as digital identity verification, tax collection, and voting systems.
Blockchain technology provides transparency, ensures accountability, and reduces the risk of fraud, particularly in voting systems where tampering with results can undermine trust in elections.
Example: Estonia has implemented a blockchain-based e-governance system that secures citizens’ health records, legal documents, and voting processes.
Financial services
Blockchain is transforming the financial services industry by enabling faster, more secure, and lower-cost transactions. For instance, decentralized finance (DeFi) applications built on blockchain allow users to lend, borrow, and trade without intermediaries.
Example: Aave, a leading DeFi platform, enables users to lend and borrow cryptocurrency directly without going through traditional banks.
Real estate
Blockchain can greatly benefit the real estate sector by streamlining the transfer of property ownership through the secure recording of deeds, titles, and contracts.
Blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries such as notaries and lawyers, reducing transaction costs and speeding up the process. Additionally, its tamper-proof nature helps prevent disputes over property rights, ensuring more transparent and efficient property transactions.
Example: Propy, a real estate blockchain platform, facilitates real estate transactions, including the sale of properties via smart contracts, reducing paperwork and delays.
Agriculture
Blockchain systems can track the journey of agricultural products from farms to consumers to ensure food safety and authenticity. At the same time, farmers can prove that their products are organic or fair-trade certified, which generally increases consumer trust and allows for more efficient supply chain management.
Example: AgriDigital uses blockchain to track grain transactions, ensuring transparency between farmers, buyers, and logistics providers.
Insurance
Insurers can automate claims processing using smart contracts on blockchain networks. Once predefined conditions are met, claims can be paid automatically. Such a setup reduces both fraud and administrative costs.
Example: Etherisc is a blockchain-based platform that automates travel insurance claims, paying out claims without needing manual verification when flight delays occur.
Media
Blockchain offers a decentralized method for content creators to distribute their work while maintaining ownership rights. Smart contracts can automate royalty payments to ensure creators receive fair compensation.
Blockchain systems can also help combat piracy by providing a transparent, immutable record of intellectual property ownership.
Example: Audius is a decentralized music streaming platform that allows artists to earn royalties directly through blockchain technology.
Cybersecurity
The decentralized infrastructure provided by a blockchain significantly enhances cybersecurity by being more resilient against attacks. The data stored on a blockchain is encrypted and distributed across multiple nodes, which makes it difficult for hackers to access or tamper with the data.
Example: Cisco integrates blockchain into its security solutions, using it to verify the integrity of devices and networks, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring data security.
Education
Blockchain offers a secure and verifiable method for storing academic records, including degrees, certificates, and transcripts. Educational institutions can use blockchain to ensure the authenticity of records, while students gain control over who can access their academic achievements.
Example: MIT issues digital diplomas on the blockchain, allowing graduates to verify and share their credentials easily.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Blockchain offers a solution to the security and scalability issues faced by IoT networks. By decentralizing control, blockchain can reduce the risk of cyberattacks, ensuring that devices can communicate securely. Additionally, blockchain ensures that data collected by IoT devices remains tamper-proof.
Example: IOTA uses a distributed ledger to secure communications between IoT devices, enabling faster and more secure data exchanges in smart cities and autonomous systems.
Blockchain challenges
Despite its many advantages, blockchain technology faces several challenges that need to be addressed for wider adoption. These challenges range from issues with scalability and energy consumption to concerns around data privacy.
- Scalability: Blockchain networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum struggle to process transactions quickly as the number of users increases. Solutions such as layer-2 scaling (e.g., Lightning Network) and sharding aim to address this problem by allowing the blockchain to process more transactions in parallel.
- Data privacy: While blockchain offers transparency, this can conflict with the need for privacy in certain applications, such as healthcare or financial transactions. Solutions like zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) allow users to prove the validity of a transaction without revealing sensitive information, but these solutions are still in development.
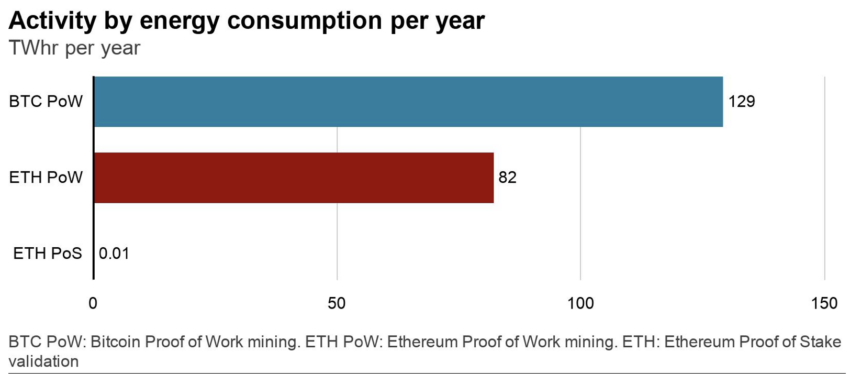
- Energy consumption: Proof-of-work networks require significant computational power to validate transactions. This leads to high energy consumption and raises concerns about blockchain technology’s environmental impact. Note that proof-of-stake and other consensus mechanisms offer more energy-efficient alternatives. The graph below demonstrates the stark difference between the two most commonly used consensus mechanisms, as well as the impact of Ethereum’s merge from the energy-intensive PoW to the significantly greener PoS.
The future of blockchain
Blockchain technology has immense potential to disrupt industries like finance, healthcare, and supply chain management, among others. However, it still faces significant challenges, such as scalability issues and regulatory uncertainty — all of which need to be addressed for its broader adoption.
In all likelihood, developments in consensus algorithms, scalability, and privacy will help blockchain overcome these obstacles over time. And as these innovations mature, blockchain’s impact will likely continue to grow across industries in the years to come.
Frequently asked questions
What is the difference between blockchain and Bitcoin?
Is blockchain secure? How does it prevent hacking?
Can blockchain be used for things other than cryptocurrency?
What are smart contracts and how do they work?
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, the educational content on this website is offered in good faith and for general information purposes only. BeInCrypto prioritizes providing high-quality information, taking the time to research and create informative content for readers. While partners may reward the company with commissions for placements in articles, these commissions do not influence the unbiased, honest, and helpful content creation process. Any action taken by the reader based on this information is strictly at their own risk. Please note that our Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers have been updated.




