Chainlink integrates real-world data into smart contracts and vice versa. The project seeks to enable secure and reliable access to real-world data and off-chain sources. This guide explains everything you need to know about Chainlink and the LINK token in 2025.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
• Chainlink is a token and software development company that takes off-chain data and compute and puts it on-chain.
• The protocol uses decentralized oracle networks, smart contracts, and the LINK token to create an efficient oracle mechanism.
• Chainlink is the most popular blockchain oracle, having secured more than 1,000 integrations and multiple partnerships.
What is Chainlink (LINK)?
Chainlink is a cryptocurrency and software technology company that deploys verifiable off-chain data and computing resources on-chain. In other words, it expands the ability of smart contracts to access real-world data that exists off-chain.
Chainlink is infrastructure that connects and validates all data, and that connects and validates all connections between chains and from chains to existing systems.
Sergey Nazarov, Chainlink Co-creator
Smart contracts are computer programs that run on a blockchain. They automate processes on a blockchain. For example, when you use a decentralized exchange (DEX) to swap one cryptocurrency for another, a smart contract automates and handles this process. In this scenario, Chainlink provides the USD pricing data. Some use cases for Chainlink are:
- Verifiable randomness
- Cross-chain transfers
- Market and data feeds (e.g., USD pricing data)
- Proof-of-reserves
Smart contracts only offer on-chain services, which limits their functionality. Chainlink is committed to creating a safe network where decentralized oracle networks (DONs) are incentivized to provide on-chain functionality to off-chain services.
Chainlink’s history
“A rising tide raises all boats,” as they say; the 2017 bull run birthed many blockchain projects, including Chainlink. In 2014, Sergey Nazarov and Steve Ellis founded SmartContract — a project that aimed to expand smart contract functionality by integrating them into external data sources.
Fast-forward to 2017, and Sergey Nazarov, a 32-year-old web entrepreneur with an in-depth knowledge of the crypto market, started Chainlink. The platform was initially built as an oracle system that settles agreements made on a blockchain.
However, Chainlink 2.0 is now considered to be the canonical version. It’s a decentralized oracle network, acting as a multifaceted abstraction layer and offering interfaces for smart contracts to extensive off-chain resources. Brief milestones in Chainlink’s history include:
- 2017: Chainlink raised $32 million during its ICO, with 1 billion LINK tokens in circulation.
- 2018: Chainlink acquired Town Crier, an authenticated data feed for smart contracts.
- 2019: Chainlink launched its platform on Ethereum’s mainnet.
- 2021: Chainlink’s project integration grew to more than 1000.
- 2022: Growth in data feeds and services
- 2023: Launched its Staking v0.2 and Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP)
How does Chainlink (LINK) work?
Firstly, users must create a requesting contract; then, real-world data is transferred to smart contracts through node operators. Chainlink registers this request as an event and then sets up a matching smart contract known as a Chainlink service-level agreement (SLA) contract, which then creates subcontracts that explain and enforce the working principles of the Chainlink protocol.
Lastly, the Chainlink node operator fulfills the request and receives LINK as compensation. To verify the authenticity of the data, the Chainlink protocol aggregates the responses from the DON and weighs each node operator’s response based on its peers. This mechanism offers an incentive market structure driving a “web of trust” and transparent reporting.
For example, if a smart contract requests the price of some asset denominated in USD terms and one node operator sends one price that is far off from the rest of the prices provided by the DON, then the protocol will select the response of a node operator from the aggregated prices of the DON.
What are oracles?
Oracles send outside-world data, such as retail payments, price feeds, and weather data, to a blockchain. Thereafter, a smart contract on the blockchain typically utilizes the data to determine whether or not to carry out a set of conditions.
Oracles read, report, and confirm real-world data for blockchains and smart contracts through web APIs or market data feeds. For instance, let’s assume Jay and Harry are betting on who will win the Super Bowl. Jay bets $1000, and Harry bets $1000, with $2000 saved in escrow by a smart contract.
When the event occurs, how does the smart contract figure out who is the winner? This is where oracles come in. They read accurate event results outside of the blockchain and report them on-chain.
Oracles form the basis of Chainlink, and it’s more of a complex oracle itself that functions as a data feed based on predetermined conditions. For example, DeFi systems like AAVE and Synthetix employ Chainlink data feed oracles to get accurate real-world prediction markets in their smart contracts.
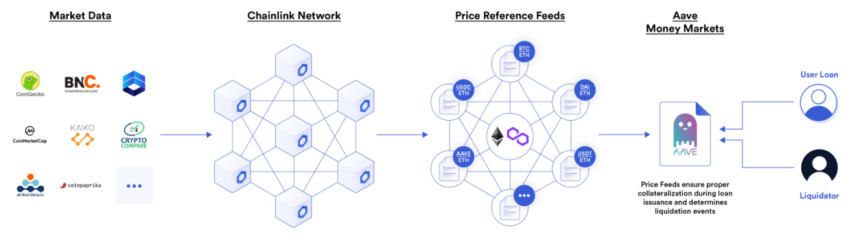
Core features
Chainlink’s primary working principle is with smart contracts. It registers a smart requesting contract as an event by setting a new matching smart contract (SLA), which provides access to any off-chain API you want to connect it to. Thus, it is possible to transact via a contract with any conventional payment network or banking system.
Below are three core features of this smart contract.
1. Reputation contract
Typically, this checks performance history and computes and records the performance history of operating nodes on the chain. This feature assures a reputation-based method that inspects, filters, and authenticates performance data on node operators and data sources by removing faulty and malicious nodes.
For example, marketplaces such as market.link provides individual data providers access to the Chainlink network to directly deploy their data on the chain via their own Chainlink nodes. Also, its analytical tools grant users access to check records on the historical performance of individual nodes.
2. Order-matching contract
This feature handles the contract query by sending and requesting to trustable nodes, checking their bids and the choices from the list obtained, and then selecting the suitable amount and types of nodes to answer the questions.
Often, the queries this contract checks are average response latency, the deviation of values in their reports from consensus values relayed on-chain, revenue generated, jobs fulfilled, and more. During this process, Chainlink converts the research contract queries into the off-chain to go into the real world and grab data from the internet.
3. Aggregating contract
Aggregating contracts validate data from both single and multiple sources. They then average the information to create a validated aggregate response, shedding away useless data.
Comparison with competitors

Chainlink is growing a solid ecosystem that is highly tamper-resistant, reliable, and future-proof. The cross-chain platform is by far the most popular Oracle network. Factors such as integration, partnerships, and market price contribute to Chainlink’s position as number one.
Chainlink has more than 1,000 integrations. These include Binance, Ethereum Classic Labs, Matic Network, Dapps Inc., and other mainstream organizations like Google, Swipe, and many more.
The closest competitor is Band protocol, which has fewer than 100 integrations and fewer partnerships. Band protocol is a community-based data resource that grants operators access to data feeds.
Chainlink differs from Band protocol in terms of operations. Band protocol allows DApp operators to access its data through its smart contract data feeds instead of Chainlink’s off-chain oracles. Other interesting oracle service providers include Witnet, API3, and WINKlink.
| Features | Chainlink | Band Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Launched | 2017 | 2019 |
| Token | LINK | BAND |
| Supported blockchains | 9 | 19 |
| Integrations | 1,000+ | 50+ |
Tokenomics
The LINK token is the native currency of the Chainlink network. This ERC-20 token runs all the operations on the Chainlink network. It is used as an incentive to compensate node operators for participating in tasks that lead to blockchain success. It has a circulating supply of over 600 million tokens.
- Max supply: N/A
- ICO price: $0.11
- Market cap: $6.4 billion
- Total supply: 608 million LINK
Where to buy Chainlink (LINK)?

The Chainlink token is supported by many exchanges, including Binance, Coinbase, and Gemini. Here, you can exchange your fiat currency, such as USD, for LINK.
To do this, you need to set up an account on one of the secure and reliable centralized exchanges. Then, verify by providing any means of identification.
Decentralized exchanges also make it easy to buy or swap other altcoins for LINK tokens. Ultimately, since it is an Ethereum-based token, you can easily purchase LINK on any Ethereum wallet like MetaMask or TrustWallet.
Price analysis and prediction
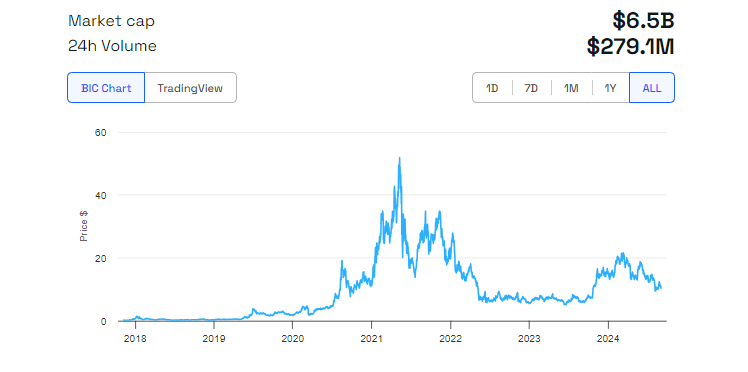
As of mid-October 2024, LINK is trading around $10 after reaching an all-time high of $54 during a brief bull season in May 2021.
Check BeInCrypto’s technical and fundamental analysis backed Chainlink price prediction for LINK’s short and long-term price potential in 2025 and beyond.
Should you buy Chainlink (LINK)?
Chainlink seamlessly integrates real-world data into blockchain technology and has proven sustainability and reliability over the years. If you’re feeling inspired enough to start investing in LINK, conduct comprehensive research before you consider adding it to your portfolio. While the project may have long-term potential, the price of crypto is highly volatile, and profits are never guaranteed.
Disclaimer: This article is written to inform and educate and should not be considered or interpreted as investment advice. Proceed with caution and DYOR before buying any crypto asset.
Frequently asked questions
What is Chainlink and why is it important?
What does Chainlink crypto do?
Is Chainlink a good cryptocurrency?
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, the educational content on this website is offered in good faith and for general information purposes only. BeInCrypto prioritizes providing high-quality information, taking the time to research and create informative content for readers. While partners may reward the company with commissions for placements in articles, these commissions do not influence the unbiased, honest, and helpful content creation process. Any action taken by the reader based on this information is strictly at their own risk. Please note that our Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers have been updated.




