Ethereum’s recent Dencun upgrade has significantly reduced transaction fees across various Layer 2 (L2) networks.
This milestone marks a pivotal moment for Ethereum users, promising improved scalability and affordability within the network.
Ethereum Dencun Upgrade: Lower Fees, More Speed
Following the upgrade, the average fee on Optimism plummeted to $0.05, while Arbitrum’s dropped to $0.5. The average transaction fee on Base fell to $0.064, while zkSyncEra’s declined to $0.161. The median fee on Optimism fell to $0.0038, while similar costs on Base, Arbitrum, and zkSyncEra fell to $0.0008, $0.3553, and $0.0936.
The Dencun upgrade went live on the Ethereum network at block height 269,568 as planned. The primary objective of this upgrade was to improve Ethereum’s scalability and affordability to enhance user experience. Central to Dencun’s efficacy is the Ethereum Improvement Proposal 4844’s (EIP-4844) proto-danksharding feature, designed to alleviate congestion by offloading obsolete data, which projects can later access through a hash.
Read more: What Is the Ethereum Cancun-Deneb (Dencun) Upgrade?
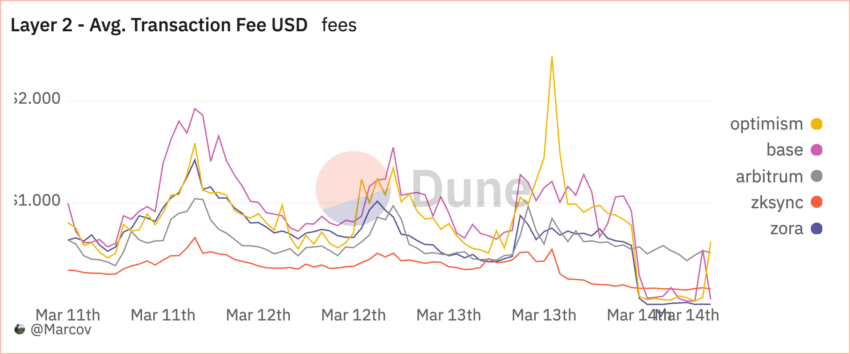
Users and experts expected that alleviating this congestion could slash Ethereum gas fees by at least ten times. Base, a prominent Layer 2 solution, initially expected that Dencun reduce transaction fees by up to 100x.
EIPs Improve Validator and Developer Experience
In addition to the significant fee reductions, the Dencun upgrade encompasses several other important Ethereum EIPs. EIP-1153 optimizes data storage and renders gas fees more economical, while EIP-7516 focuses on returning the base fee of blobs of a current transaction block.
EIP-4788 and EIP-5656 enhance data accessibility and memory copying within Ethereum’s execution layer. Meanwhile, EIP-6780 introduces measures to protect user funds by halting smart contract execution.
EIP-7044 and EIP-7514 pertain to the administration of validators responsible for network security. Finally, EIP-7045 extends the time frame for attestations to be included in transaction blocks.
Read more: A Deeper Look Into The Ethereum Network
Ethereum developers subjected the different Ethereum EIPs to rigorous testing before deploying the Dencun upgrade to the Ethereum mainnet. They first deployed Dencun on the Goerli testnet on January 17, 2024, before transitioning to the Sepolia testnet on January 31 and the Holseky testnet one week later. Only after rigorous testing on the third testnet did the Dencun upgrade receive the green light to be deployed on the Ethereum mainnet.
Disclaimer
In adherence to the Trust Project guidelines, BeInCrypto is committed to unbiased, transparent reporting. This news article aims to provide accurate, timely information. However, readers are advised to verify facts independently and consult with a professional before making any decisions based on this content. Please note that our Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers have been updated.


