Chinese researchers have created a quantum computer ten billion times faster than Google’s prototype. We explain why this is important and what it means for the crypto sphere.
What are quantum computers?
A quantum computer is a super powerful calculating machine that can process information about 100 trillion times faster than a traditional computer. This kind of power comes in handy when processing large amounts of data, modeling circuits, and many more possibilities that will only be discovered in time.
However, this technology has a dark side. Researchers believe that quantum computers can completely dismantle computer security as we know it. With such powerful data processing power, no code will take more than a moment to analyze. This means, quantum computers can read terabytes of data in just second and thus break cryptographic code.
For example, bank transactions and messages are encrypted with the help of the RSA algorithm. To break RSA would take a normal computer hundreds if not thousands of years. A quantum computer can break RSA cryptography in minutes.
Elaborating on the progress of research on quantum computers, Mark Mattingley-Scott, IBM Q Europe Ambassador, said:
“We’re now at the stage where we have quantum computers and we’re able to use them. We’re able to program them. We’re searching for a way to make it more industrializable and stable, and for robust technologies. We’re learning how to write algorithms for them. We’re working on different types of quantum computing.”
Mattingley-Scott is sure that humanity is ready for machines like this. He also believes we are ready for the consequences.
How quantum computers work
A quantum computer, in contrast to a traditional one, operates not with bits or bites (one unit of information in a double system of calculation) but with quantum bits, or qubits. This technology speeds up computer processing hundreds of times.
The hardware is also more complex than that of its predecessors. There are more parts than a traditional computer and it must be supercooled constantly.
What quantum computers are on the market?
Prototype quantum computers appeared at the end of the 20th century. In fall 2019, Google presented their most recent development and demonstrated the massive possibilities of quantum computation.
A NASA experiment showed that the machine needed three minutes and 20 seconds to do the same calculations that would take the most powerful traditional supercomputer at the time 10,000 years.
For unknown reasons, NASA deleted their report, but journalists at The Financial Times were able to maintain a copy.
At the start of December 2020, a new, even more powerful quantum computer appeared. It was created by a group of Chinese scientists under the leadership of well-known physicist Jianwei Pan.
Results of their experiments in the journal Science showed that the productivity of the new computer was superior to Google’s computer by a factor of ten billion, and traditional supercomputers by a factor of 100 trillion.
Researchers did not say how much a quantum computer of this caliber might cost.
Quantum computers in government service
Researchers of the new quantum computer believe that the creation of the machine comes close to “Quantum Supremacy.” A superiorly productive computer that could quickly solve very difficult jobs could give the country an advantage in a variety of fields, from chemistry to artificial intelligence (AI) to big data analysis.
Quantum supremacy means that a computer can do calculations which are essentially impossible for a traditional computer to do in a reasonable amount of time.
In the video below, Pan equates the achievement of “Quantum Communication” made possible by his research with the development of human civilization.
The researcher explained that 100,000 years ago, Homo sapiens became victorious in the struggle of evolution over Neanderthals because of their ability to communicate and share information.
In the 21st century, people continue to develop communication, but now they do it at the quantum level. Pan is sure that work in this field will be the basis for the future evolution of humanity.
How quantum computers became miner enemy #1
Holding a superior calculating machine could give a person or a group an advantage in, or even control of, a network, putting the crypto mining industry under threat.
Mining requires high-power equipment. Crypto asset miners use the computing power of their own computers to solve mathematical problems. Some run conventional computers, while others purchase special equipment for crypto mining called application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs).
Whoever solves the mathematical problem first gets the block reward, and the more powerful the computer, the higher the chances it has to solve the problem and get the reward paid in bitcoin (BTC). Sometimes miners join forces and solve problems together. The only downside — profit has to be split amongst the members of the pool.
But miners are scattered across the globe, and that is how the decentralization of crypto is achieved.
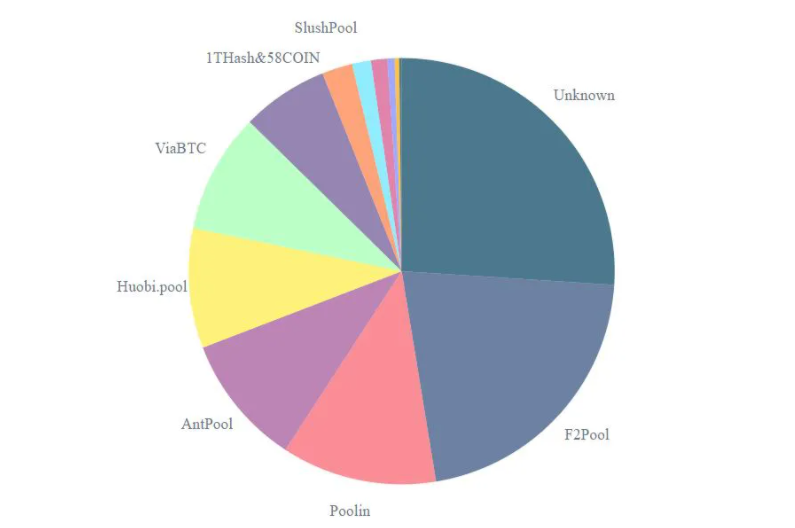
The pie chart clearly shows that the activity of bitcoin miners is spread between individuals and large pools. They all compete for the right to claim their prize, that is why there is no one “leader.”
The collective volume of calculating power that miners use on the Bitcoin network is called the hashrate. Thanks to the rivalry that the competition brings, the playing field is basically level. Everyone is working with basically the same equipment, at least proportionally.
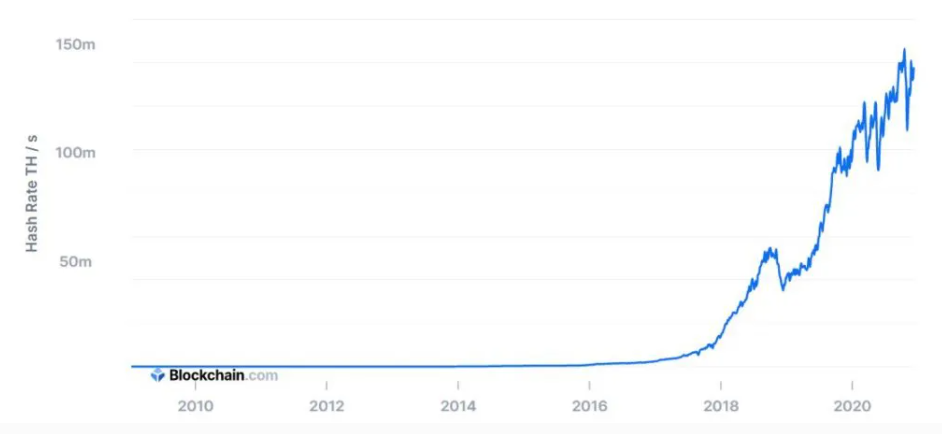
But quantum computers are on a completely different level of calculating power. They can disrupt the balance. A quantum computer in the right hands could take 51 per cent of bitcoin’s hashrate, known as the 51 per cent attack. That would basically give the quantum computer owner total control over the cryptocurrency market.
A power grab like that would destroy the ability of the network to function properly and would block transaction confirmations. What’s more, a 51 per cent attack brings the threat of a “double spend.” A double spend can reverse already confirmed transactions.
To make an attack like that a reality using normal computers and ASICs would require a colossal amount of resources, both monetary and electric. A quantum computer connected to a cryptocurrency network could complete that kind of attack quick and cheap.
Why quantum computer tech is a threat to cryptocurrency
Grabbing the majority of bitcoin’s hashrate, or the hashrate of other cryptocurrencies, which uses cryptography, could mean a crypto project’s ruin. Only a user or a group of users who had comparable computing power would be able to resist such an attack.
In practice, this kind of scheme is unlikely to become a reality. The problem is that purchasing a quantum computer today to become a crypto criminal is basically infeasible. At the same time, an attack on the Bitcoin network with quantum equipment could be fatal.
According to analysts at Deloitte, a quantum computer could be used to steal cryptocurrency, through the use of the massive computing power to get passwords or codes. To be more precise, investigators came to the conclusion that the level of threat would depend on the type of coin. They believe that at least 25 per cent of bitcoin is at high risk.
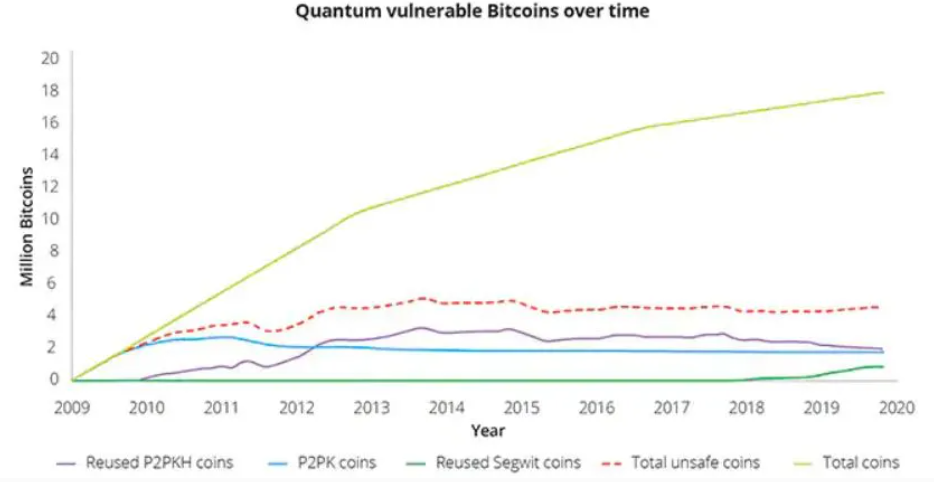
CEO of the British cryptography company Post Quantum, Anderson Cheng, for his part, noted in a Decrypt interview that the crypto community should try to develop tools to stand up against quantum burglary. Otherwise, in his opinion, the destructive power of these machines could annihilate bitcoin.
Interesting fact! Currently, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is developing post-quantum cryptography algorithms. With this group’s help, in theory, a cryptocurrency could fork into a quantum-resistant branch of the blockchain. This new “branch” could continue to work on the basis of a quantum-resistant algorithm.
The fruit of NIST’s work could appear on the market as soon as 2022. Before that, the crypto community will be stuck in “quantum uncertainty” about its future.
Regardless of that degree of risk, at some point, the community could come to a consensus that quantum computers simply create too much of a risk to bitcoin.
What else is the crypto community afraid of?
Recently, a popular crypto analyst, the author of Plan B’s S2F — Forecasting Models, did a survey among his readers. The main question was about the risks that bitcoin might face.
Quantum computers, regardless of their destructive power, were only the second biggest worry. The scariest threat to bitcoin, according to the crypto community, was regulatory pressure from the powers that be. The rest of the dangers facing bitcoin included:
- Centralized mining. The problem is that higher than 70 per cent of bitcoin’s hashrate comes from China. If the country’s government takes control of local miners, the network could come under threat.
- Hacks, bugs, and cybercriminals.
- Financial derivatives.
- Forks — that is, new improved versions of BTC.
The crypto community is split into two camps: one thinks that quantum computers pose an existential threat to digital assets, while the other does not see the danger.
Despite the fact that, for now, quantum computers only function at the behest of large research groups and governments, it cannot be ruled out that the future may bring retail quantum machines to masses, or at least the criminals.
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, this price analysis article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial or investment advice. BeInCrypto is committed to accurate, unbiased reporting, but market conditions are subject to change without notice. Always conduct your own research and consult with a professional before making any financial decisions. Please note that our Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers have been updated.


