Storing critical data in one singular place can leave a company vulnerable to hacks, corruption, or even system failures. Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) solves this traditional data management problem by decentralizing data storage. DLT ensures security, transparency, and easy access — all without a central authority. This guide explains how. Here’s what to know about DLT in 2025.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
➤ Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) secures and decentralizes data, making transactions transparent and tamper-proof.
➤ While blockchain is a popular form of DLT, other version of the technology can offer faster transactions and more customization.
➤ DLT adoption is expanding across industries like finance, healthcare, and supply chains, transforming digital record-keeping.
What is Distributed Ledger Technology?

Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is a digital system suitable for recording, sharing, and synchronizing data across multiple devices in various locations.
In simpler terms, it’s like having a spreadsheet that everyone in your team can access, update, and verify without a manager overseeing every change.
How DLT differs from centralized ledgers
In centralized systems, all data is stored in one place, like a single bank that controls everyone’s transaction records. If the bank’s system crashes, the data is at risk.
DLT solves this by distributing data across multiple nodes, or individual devices, connected in a network. Each node has its own copy of the ledger and validates updates through a consensus mechanism, ensuring no single point of vulnerability.
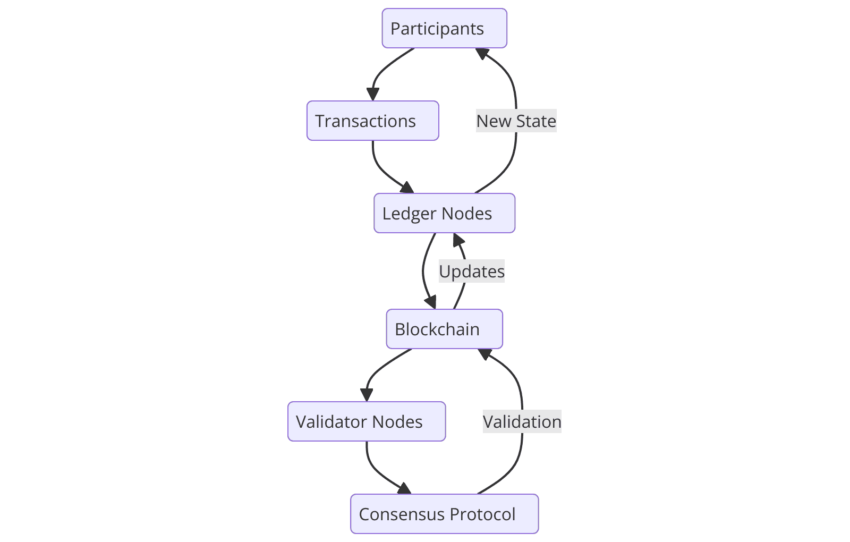
Components of DLT
To understand DLT, think of three main components:
- Nodes: These are the individual devices (computers or servers) that store a copy of the ledger.
- Consensus mechanisms: These processes ensure that all nodes agree on the changes made. This happens via different methods, such as proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS).
- The concept of immutability: Once data goes into the ledger and is verified, it cannot be altered. This makes DLT highly secure and tamper-proof.
Imagine a traditional ledger like a classroom attendance register. Only the teacher keeps the book, and if it’s misplaced or someone sneaks in to change a record, the class has no way to verify what’s true.
In contrast, DLT is like giving every student a copy of the register. Everyone has to agree upon any change before it’s made — making tampering almost impossible.
Did you know? In Italy, 95% of banks now use a DLT platform to automate interbank reconciliation, reducing manual interventions to just 1% and enhancing overall efficiency. Similarly, major players like DTCC and Euroclear are testing DLT’s capabilities to improve trade settlements and streamline data transparency.
How Distributed Ledger Technology works
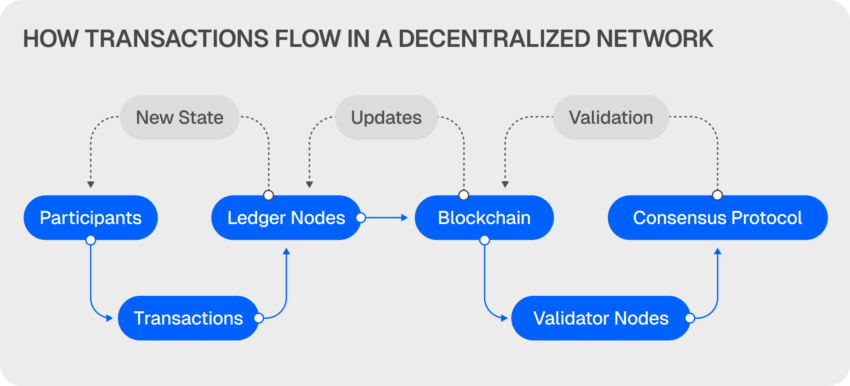
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) works by storing, sharing, and validating data across multiple nodes in a decentralized network.
Instead of relying on a single central authority, DLT uses peer-to-peer interactions and consensus mechanisms to confirm transactions, ensuring that every participant has a consistent view of the ledger. This allows for secure data exchanges without a middleman.
The data flow is as follows:
- Data entry: A new transaction or record is initiated and broadcast to the entire network of nodes.
- Validation through consensus mechanism: Each node follows a set of rules (consensus mechanisms like proof-of-work or proof-of-stake) to validate the transaction. Majority agreements are required.
- Synchronization and ledger update: If the transaction is valid, it’s simultaneously updated on all nodes, making the data consistent across the network.
- Data immutability: Once recorded, the transaction cannot be altered or deleted unless all nodes agree, ensuring a tamper-proof system.
In 2024, the European Union started a pilot project using DLT for cross-border digital identity verification. The project, named EBSI (European Blockchain Services Infrastructure), enables citizens to share verified identities securely across E.U. member states. This DLT-based approach protects personal data and allows faster cross-border services and reduces costs.
DLT vs. blockchain
While both Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) and blockchain serve as decentralized systems for recording data, they aren’t the same thing. It’s like the relationship between rectangles and squares — all squares are rectangles, but not all rectangles are squares. Similarly, while all blockchains are distributed ledgers, not every distributed ledger uses a blockchain structure.
To clear this out, here is a quick table that you can refer to:
| Feature | Blockchain | Distributed Ledger |
| Structure | Sequential chain of blocks | Can vary (DAG, traditional ledger) |
| Consensus mechanism | Often uses PoW, PoS, or similar consensus models | Potentially faster with fewer nodes |
| Immutability | High | Moderate (depends on the type) |
| Transparency | Public and visible | Can be private or permissioned |
| Speed | Slower due to validation | Potentially faster with fewer nodes |
2024年、食品業界では、DAGベースの分散型台帳を活用したサプライチェーン追跡において大きな進展が見られました。ネスレを含む企業は、農場から店頭まで食品製品を追跡するためにDLTを利用し、遅延を20%削減し、不正のリスクを最小限に抑えることに成功しました。
Key features of Distributed Ledger Technology
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) has several distinct features that make it a reliable solution compared to traditional systems. Here is the lowdown:
- Decentralization: Instead of being stored in a single, central location, data is spread across multiple nodes in the network, minimizing the risk of a single point of failure and eliminating intermediaries.
- Consensus mechanisms: Transactions are validated using consensus methods like proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS), ensuring that all nodes agree on the transaction’s validity before it’s recorded.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is verified and added to the ledger, it cannot be changed or deleted, creating a permanent and tamper-proof record.
- Transparency: Every participant has access to the same copy of the ledger, making the transaction history visible and easily auditable.
- Data security: Cryptographic techniques such as hashing secure data, making it resistant to unauthorized changes or hacking attempts.
- Peer-to-peer interactions: Participants conduct transactions between each other without needing a central authority, reducing costs and increasing transaction speed.
- Smart contract functionality: Some DLT systems, like blockchains, support smart contracts — self-executing contracts that automatically enforce the terms of an agreement when specific conditions are met.
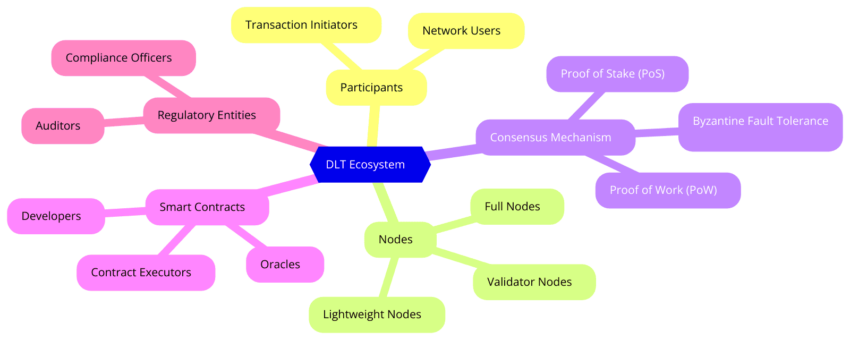
Benefits of DLT
The primary benefits of DLT include:
- DLT provides an open view of transaction history, making it easy to track and verify data across all nodes in the network.
- Cryptographic methods and consensus mechanisms protect the data, ensuring that it’s resistant to unauthorized access or alterations.
- By eliminating intermediaries and automating processes, DLT significantly lowers operational costs for businesses.
- Faster processing and settlement times result from direct peer-to-peer transactions and smart contract functionality.
- The immutable nature of DLT ensures that once the contract validates the record, it remains unchanged, which is ideal for maintaining accurate records over time.
- With a transparent, secure, and tamper-proof system, DLT helps establish trust among participants without needing a central authority.
- Some DLT models offer the ability to scale efficiently, supporting high transaction volumes without compromising performance.
It is now time to see how these benefits add up in real life. Here are a number of practical scenarios where DLT is applied across industries in 2025.
Applications of Distributed Ledger Technology
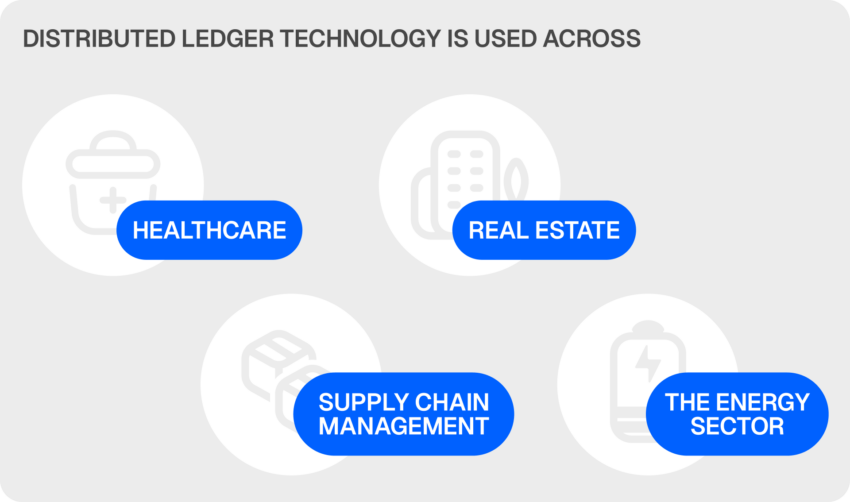
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) has made real-world advancements across multiple sectors. Here’s how different industries are leveraging DLT.
- Healthcare: DLT helps manage patient data securely, giving patients more control over their records.
For instance, BurstIQ uses DLT to create secure profiles for patients, allowing health providers and researchers to access only the necessary information with user consent. This approach streamlines data sharing, improves patient privacy, and reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
2. Supply chain management: DLT enhances transparency in tracking the movement of goods across complex supply chains.
Take Nestlé, which uses a blockchain-based system to track milk and palm oil supply chains from farms to supermarkets. The technology helped reduce delays by up to 20% and improved traceability, helping ensure that products are ethically sourced and safe.
3. Real estate: DLT can transform real estate by enabling secure, transparent, and faster property transactions.
In 2024, Propy, a blockchain-powered real estate company, facilitated a $1.6 million property deal entirely through a blockchain platform. This transaction minimized paperwork, eliminated intermediaries, and cut down the processing time by more than 30%.
4. Energy sector: DLT supports peer-to-peer energy trading, which enables consumers to buy and sell excess renewable energy directly.
LO3 Energy, a company based in Brooklyn, New York, has developed a blockchain platform for local energy trading. The system allows households with solar panels to sell surplus power to their neighbors, promoting sustainability and reducing dependence on traditional energy suppliers.
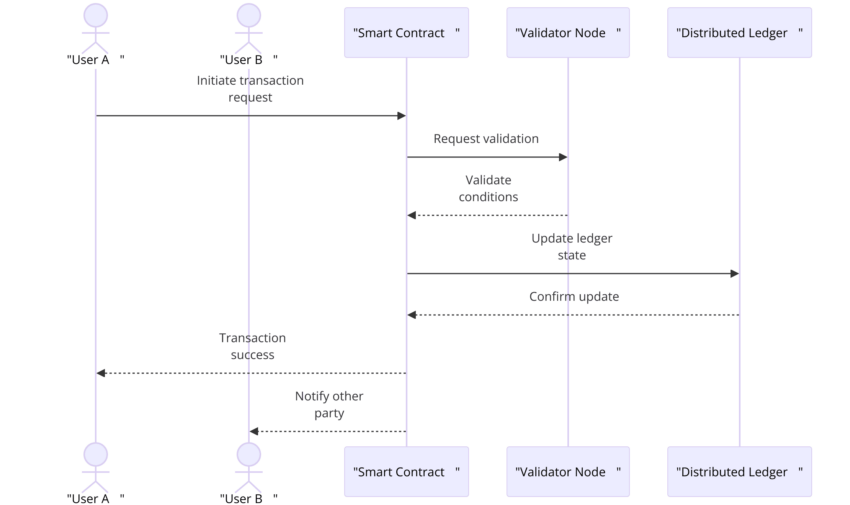
Challenges and limitations of DLT
Despite the potential, Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) faces several challenges that can limit its widespread adoption and usability:
- Scalability: DLT struggles with handling a high volume of transactions due to the consensus mechanisms, leading to slower processing times and higher costs.
- Interoperability: Different DLT platforms often cannot communicate or integrate with each other, making cross-platform transactions and data sharing complex.
- Regulatory uncertainty: Lack of clear regulations and varying laws across regions can hinder DLT adoption, especially in industries like finance.
- Energy consumption: Some consensus mechanisms, like proof-of-work (PoW), consume large amounts of energy, making certain DLT models less sustainable.
- Data privacy: While DLT offers transparency, it can conflict with privacy requirements in industries like healthcare, where sensitive data needs protection.
- The complexity of implementation: Setting up and maintaining a DLT system requires significant technical expertise, making it challenging for non-technical businesses to adopt.
Despite these challenges, DLT continues to make waves in the technological space in 2025.
What’s the future of DLT?
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is slowly becoming a cornerstone of digital transactions across various sectors. With improvements in scalability, clearer regulations, and expanding use cases, DLT will likely continue transforming data security, transparency, and trust in 2025 and beyond. As more industries adopt the technology, DLT will redefine how we manage digital records and agreements, paving the way for a decentralized digital future.
Frequently asked questions
What is Distributed Ledger Technology?
How is Distributed Ledger Technology different from blockchain?
What industries use Distributed Ledger Technology?
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, the educational content on this website is offered in good faith and for general information purposes only. BeInCrypto prioritizes providing high-quality information, taking the time to research and create informative content for readers. While partners may reward the company with commissions for placements in articles, these commissions do not influence the unbiased, honest, and helpful content creation process. Any action taken by the reader based on this information is strictly at their own risk. Please note that our Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers have been updated.




