Crypto airdrops are used by many projects, from start-ups to well-established businesses. Projects are only successful if they attract and maintain an active user base. An airdrop is effectually a marketing strategy to raise awareness of a new currency. Here’s a quick rundown of what crypto airdrops are and how they work in 2025.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
► Airdrops are a common strategy for distributing tokens to the community to increase awareness and encourage user engagement.
► Airdrops help projects mitigate the risks of low token float by increasing token circulation, which can stabilize prices and reduce volatility.
► Although airdrops can boost metrics, these gains may be short-lived as many users exit after receiving the free tokens.
► Airdrops carry potential risks, including Sybil farming, pump-and-dump schemes, and low-quality user retention.
What is a crypto airdrop?

An airdrop is a process where a blockchain or crypto project distributes free tokens or coins directly to the digital wallets of its community members. This is often done as a promotional strategy or as part of a token distribution plan.
Crypto airdrops have a few advantages, such as brand exposure; you get the word out, reaching a large number of people. You also get wide distribution because ICOs have a very limited number of investors. So, airdrops enable more people to own your cryptocurrency.
Morten Christensen, Founder & CEO of AidropAlert: Youtube
A key component of airdrops is that the tokens received are free. Lockdrops are similar to airdrops but differ in that they are a method used to distribute tokens across a broad network. They’re akin to initial coin offerings (ICOs), but they distinguish themselves by not requiring the raising of funds. This shouldn’t be confused with a crypto airdrop.
BeInCrypto Bonus Hunter | All-in-One Crypto Rewards Hub
Here you can find all Crypto Airdrops from various crypto exchanges: Use this link
History of airdrops
Airdrops have an interesting history. Here are some of the most prominent events that have shaped the way founders and creators distribute cryptocurrency today.
Auroracoin (AUR)
Many people regard Auroracoin (AUR) as the first cryptocurrency airdrop. Auroracoin was a cryptocurrency exclusively for Icelandic residents. It was an alternative to the country’s fiat currency.
As part of the experiment, Auroracoin’s inventors gave AUR tokens to Icelandic people in what is considered the first airdrop in 2014. Each Icelandic citizen with a valid ID was entitled to receive 31.8 AUR.
This airdrop’s purpose was to encourage adoption and raise awareness of the cryptocurrency by giving it directly to individuals, eliminating the requirement to purchase or mine it.
Uniswap (UNI)
Uniswap is one of, if not the most, popular decentralized exchanges on Ethereum and in crypto altogether. It introduced its governance token, UNI, in September 2020 through a now highly regarded airdrop.
Uniswap distributed 400 UNI tokens to every Ethereum wallet that had interacted with the Uniswap protocol before Sep. 1, 2020. This airdrop generated a lot of attention because:
- The value accrued by the UNI tokens
- It showed that decentralized applications (DApps) can reward their users directly
- Gave users governance power over the protocol
How do airdrops work?
Several steps involve distributing a crypto airdrop. They typically require a combination of smart contracts, data collection, and some distribution mechanism.
Before you can distribute tokens, you must first define the criteria to determine who qualifies. For example, you can airdrop tokens to other token holders, reward users who have interacted with specific smart contracts of DApps, target new wallets, etc.
The Starknet airdrop introduced a novel criterion that allowed even Github developers who made commits within a certain time frame to claim STRK. Virtually any parameter you can think of, or that is enforceable on the blockchain can be used to distribute crypto.
Some projects require users to claim tokens by interacting with a smart contract, while others distribute tokens directly into users’ wallets.
One benefit to airdrops is that they help mitigate the risks of a low token float by increasing the number of tokens in circulation, reducing price volatility.
A low float can result in extreme price swings since even small trades can have a large impact. By distributing tokens through airdrops, protocols increase market liquidity, helping to stabilize the token’s price relative to its fully diluted valuation (FDV).
Crypto points
A popular way to define criteria for crypto airdrops is the points system. Crypto points are a system where certain types of behaviors or actions are assigned a value or points. These points can be converted into crypto later. Or, in some scenarios, founders use points to weed out Sybil farmers.
Sybil is a term that was taken from a popular book by the same name. Sybil farming is an event where someone creates multiple addresses to collect an airdrop and earn more crypto than is allotted for a single address or wallet.
The points system is a way to influence behavior. For instance, you may receive a lot of points for having a high transaction volume. On the other hand, you may also receive points for completing a single, low-value transaction.
While both actions give you points, this does not necessarily mean that they are useful. The user who creates a lot of transactions with low values may receive less or no crypto because they have a lot of points for that particular action.
Snapshots
A crypto snapshot is an event that occurs before an airdrop and creates a record of all the accounts eligible for the airdrop. The snapshot occurs at a specific block height or date. Because a blockchain is effectually a ledger, this process is verifiable on-chain. To collect these addresses, many projects use scripts to query the blockchain.
When and why does a crypto airdrop occur?

A crypto airdrop typically occurs when a project wants to generate excitement and create awareness for its token or platform. Airdrops are a popular method used by new projects to attract attention, often distributing tokens for free to existing holders of a specific cryptocurrency or users of a platform.
For example, if a new project wants to siphon users from a similar protocol, it might airdrop its token to all the token holders of its competitor to gain initial traction.
Another common reason for airdrops is to reward loyal and early adopters. By offering free tokens, projects incentivize users to engage with their platform while promoting long-term loyalty.
Airdrops also allow participants to become stakeholders in the project’s future success, often by giving them voting rights or governance tokens.
Lastly, airdrops can also serve as an alternative to initial coin offerings (ICOs) and similar practices, which are banned or heavily regulated in some countries. Airdrops allow projects to distribute tokens without raising funds directly, avoiding regulatory hurdles that ICOs might face.
Different types of crypto airdrops

1. Standard airdrop
With standard crypto airdrops, one needs to sign up ahead of time. Generally, the project announces its airdrop and asks users to sign up using various methods. Once the airdrop date occurs, the assets will be sent to those who qualify.
2. Surprise airdrop
Surprise crypto airdrops are just that — surprises! Basically, one day, a user will wake up to find a new token in their wallet. The idea is to create awareness of a new asset, hoping free assets will entice the user to the network.
3. Exchange airdrop
Similar to the previous two airdrops, an exchange airdrop differs in that it’s trying to generate trading volume. The 1inch exchange held an airdrop, providing its tokens to traders on the Uniswap platform. Their goal? Bring traders over from a competitor’s exchange.
4. Smart airdrop
Smart airdrops are essentially targeted airdrops. They analyze the type of user that would be most interested in the project, looking at things like demographics and user interests before distributing the tokens in a more directed manner. The BitTorrent airdrop for Tron holders, for instance, designated about 90 billion BTT tokens to TRX holders.
Drawbacks of crypto airdrops

While crypto airdrops sound like a win-win for both parties, there are some drawbacks to such a method. These drawbacks can apply to either airdrop farmers or the platforms distributing the airdrops themselves.
Low-quality user-retention
For a project, airdrops seem like a no-brainer marketing scheme. You can create a token virtually out of thin air at little to no cost. The downside is that when building a serious platform, the users may only be there for the tokens. After the user collects the tokens, they may no longer use the platforms.
This scenario defeats the purpose of using airdrops as a marketing mechanism. The best way to circumvent this phenomenon is to provide real value and cultivate users who are actually interested in your project.
Vanity metrics
When users do exit the platform after receiving the airdrop, activity drops. Before this, the platform may experience a boost in activity, TVL, or market cap.
This makes it seem like the platform is well-used. This is important because some crypto businesses often use these hyper-inflated metrics to receive venture capital funding.
Imagine if you wanted to invest in a business and you found out that they did not make as much money or have as many users as they say they did after you already invested money. Be aware that tools like airdrops can be used to pump the metrics on some platforms.
Sybil farming
Some users like to engage in Sybil farming or airdrop farming. This simply means that they create a lot of accounts on the blockchain to become eligible to receive more crypto in an airdrop.
Some airdrops may limit the amount of crypto that one address can receive. To circumvent this, farmers create multiple accounts or bots.
There are a few ways to prevent farming. Jito Labs and LayerZero created interesting ways to filter Sybil farmers, the latter of which employed a Sybil self-reporting mechanism. However, it is virtually impossible to get rid of Sybil farmers without proof of personhood.
Pump and dumps
A pump-and-dump scheme occurs when someone creates a project and a token only to abandon both after the price increases. This can also apply to traders who may promote or pump the price of a token only to sell it to new traders to make a profit.
Most tokens received after an airdrop lose their long-term value, leading to criticisms of their utility. According to data from CoinMetrics, most airdrop token holders liquidate their crypto shortly after they receive it.
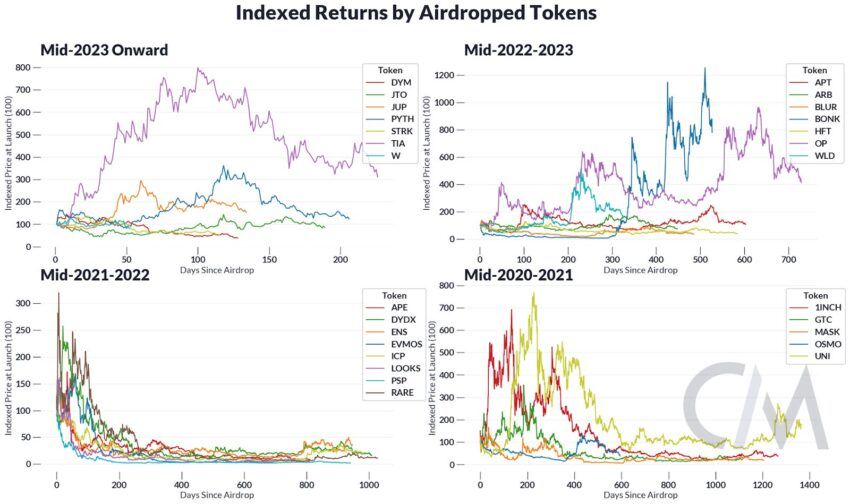
Crypto airdrops pros and cons
Here’s a quick summary of the pros and cons of crypto airdrops.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Marketing tool for businesses | Pump and dumps |
| Free tokens for users | Sybil farming |
| Mitigates low token float | Low-quality user-retention |
| Rewards loyal users | Vanity metrics |
| Helps influence platform behavior | Scams, regulatory, and tax risks |
Avoid scams with crypto airdrops
The viability of crypto airdrops in recent times has often been contested. On the one hand, users often treat them as an entitlement, and when expectations are unmet, relations are sour, regardless of the project’s viability. On the other hand, airdrops are still a useful way to reward loyal customers and users who genuinely care about a project or platform.
Ultimately, airdrops remain a double-edged sword, and both users and project founders must approach them strategically, balancing rewards with long-term sustainability. Always prioritize your safety and security when claiming or interacting with airdrops, as they can be used as a relatively sophisticated scamming tool.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice. Crypto airdrops can be scams. Be sure to vet projects thoroughly and only ever click on official links. Never share your personal details or private keys.
Frequently asked questions
What is an airdrop?
How do you receive a crypto airdrop?
Can you make money from airdrops?
Are airdrops safe?
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, the educational content on this website is offered in good faith and for general information purposes only. BeInCrypto prioritizes providing high-quality information, taking the time to research and create informative content for readers. While partners may reward the company with commissions for placements in articles, these commissions do not influence the unbiased, honest, and helpful content creation process. Any action taken by the reader based on this information is strictly at their own risk. Please note that our Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers have been updated.


