As blockchain adoption grows, so do risks like frontrunning attacks, token scams, and cross-chain vulnerabilities. Blockchain security protocols are crucial in this regard, ensuring that every step of a transaction — from initiation to confirmation — is protected. Understanding end-to-end transaction security is key for users and developers to avoid losses and ensure safe, uninterrupted network interactions. This article explores the top protocols ensuring secure blockchain transactions in 2025.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
➤ Blockchain security protocols like Omnia, LayerZero, Chainlink CCIP, Cosmos IBC, and Wormhole ensure end-to-end transaction security by protecting data from manipulation and preventing incomplete transfers.
➤ End-to-end transaction security ensures no unauthorized entity can interfere with or alter a blockchain transaction.
➤ While the listed protocols provide critical security, continuous audits, smart contract checks, and vigilant user behavior, all remain essential to countering evolving risks in decentralized networks.
Top 5 blockchain protocols
In brief, some of the top blockchain security protocols in 2025 include:
- Omnia Protocol – Frontrunning protection with private mempools
- Graphite Network – Leading in Reputation-Driven Access and Private Identity Verification
- LayerZero – Private relayers for secure cross-chain communication
- Chainlink CCIP – Multi-layer validation for token transfers
- Wormhole – Guardian nodes for cross-chain transaction safety
- Cosmos Hub (IBC Protocol) – Secure asset transfers with Tendermint consensus
Let’s examine each blockchain security protocol in detail.
1. Omnia Protocol: Best for preventing exploits
Omnia Protocol ensures that blockchain users and developers enjoy secure and private access to networks without fear of frontrunning, token scams, or malicious interactions.
By safeguarding transaction data from initiation to completion, Omnia delivers end-to-end security and keeps every blockchain operation confidential.
How it works?
Omnia acts like a guarded tunnel for blockchain transactions. When a user interacts with a blockchain through Omnia’s private RPC endpoints, the data is hidden from public view, protecting it from attackers. These private mempools prevent bots from frontrunning trades or intercepting sensitive information.
In addition, Omnia detects honeypots — scam tokens designed to trap users — by analyzing smart contracts and transaction data in real-time.
If a malicious token is detected, Omnia halts the transaction, ensuring user funds remain secure. This multi-layered security ensures that every blockchain transaction is completed safely without vulnerabilities being exposed.
Omnia is also blockchain-agnostic and supports continuous transaction monitoring and multiple networks, ensuring the broadest possible security coverage.
Pros
- Prevents frontrunning attacks: Private RPCs keep transactions hidden from bots.
- Blocks scam tokens: Honeypot detection stops users from interacting with fraudulent tokens.
- Multi-chain support: Works across several blockchains, ensuring flexibility.
Cons
- Technical setup: Users may need time to understand private RPCs and honeypot protections.
- Node dependency: Requires consistent participation from nodes for uninterrupted access
2. Graphite Network – Leading in Reputation-Driven Access and Private Identity Verification
Graphite Network is a layer-1 blockchain that formalizes interactions through a reputation-based system, bringing the benefits of traditional finance together with the transparency and security of blockchain. Additionally, it employs a KYC mechanism that enhances transaction security.
How it works
Graphite Network is built around one core idea: reputation should shape how we interact on-chain. Every user has a blockchain-visible Trust Score, calculated from behavior, longevity, KYC level, and transaction patterns, offering a powerful, transparent way to gauge credibility before transacting. This trust layer is foundational for secure onboarding, peer-to-peer reliability, and DApp interaction.
Graphite Network also supports reputation-based smart contracts, giving developers the flexibility to set custom rules and tailor access to services or rewards. For example, users with higher trust scores or verified credentials can be offered better fees, access tiers, or bonuses. An upcoming feature, tagged addresses, will further enhance this by letting wallets carry contextual labels, like “charity” or “business”, which makes interactions clearer and more meaningful.
To strengthen this model without compromising user privacy, Graphite Network separates identity verification from the chain. KYC processes happen off-chain, while Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZKP) technology enables users to prove compliance without revealing personal data. Only the wallet’s final KYC level is recorded on-chain, allowing for trust-based interactions without exposing sensitive information. Users can also apply filters to avoid interacting with accounts that fall below certain KYC thresholds.
Graphite Network’s “one user, one account: policy, combined with a small setup fee paid in its native coin, @G, further protects against identity spoofing, multi-account abuse, and sybil attacks, reinforcing the integrity of its reputation system.
The blockchain runs on a PoA Polymer 2.0 mechanism, delivering 1,400 transactions per second, more than three times PayPal’s throughput, while remaining eco-friendly thanks to its non-mining architecture.
While most blockchains use similar node structures, Graphite Network distinguishes itself by rewarding both entry-point and authorized nodes directly from the blockchain. Entry-point nodes, which are open to anyone, can earn a share of transaction fees. Authorized nodes, responsible for block production and subject to compliance checks, also receive on-chain rewards. This native earning model supports a more inclusive and sustainable network, where participation is incentivized not by speculation, but by real contribution and trustworthiness.
Pros
- Built-in reputation and trust scoring enable customized access controls and risk-based transaction policies
- Users can run their nodes, recouping the relay fees for sending their own transactions
- Graphite Network is EVM-compatible, making deploying Ethereum applications and smart contracts simple
Cons
- One-time setup fee is required to activate an account, but it’s minimal and designed to deter abuse, not access
- Newer ecosystem compared to Ethereum or Solana, so tooling and integrations are still growing
3. LayerZero: Best for secure cross-chain transactions
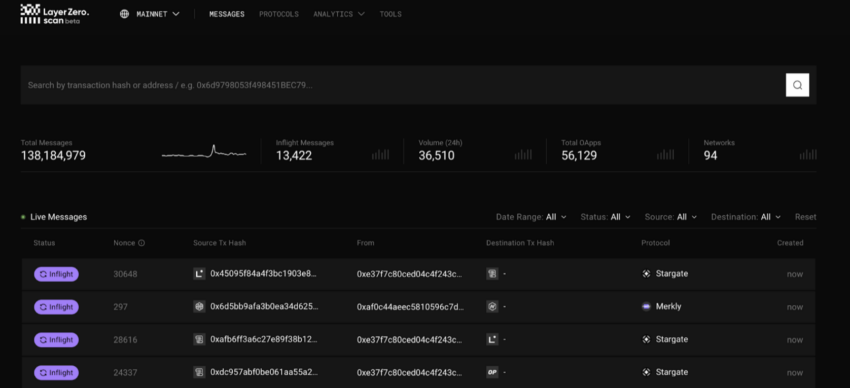
LayerZero ensures that transactions between different blockchains are completed safely and without interruption. Cross-chain transactions often introduce new risks, such as frontrunning and incomplete transfers, but LayerZero eliminates these vulnerabilities by securing every part of the transaction — from initiation on one blockchain to confirmation on another.
How it works?
LayerZero maintains speed and security by using a combination of ultra-light nodes (ULNs), oracles, and relayers. Think of it like sending a package through a trusted courier network, where the couriers (relayers) and validators (oracles) confirm that the package reaches its destination intact without interference from outsiders.
Ultra-light nodes (ULNs) validate transactions without requiring the entire blockchain’s data, which keeps the network agile while maintaining security.
Relayers transmit the transaction data between blockchains while keeping it hidden from public exposure, ensuring that no one can intercept the data or manipulate the transaction.
Oracles independently verify transactions at both the source and destination chains, maintaining data integrity even during cross-chain swaps.
By separating the validation and relay roles, LayerZero ensures that a compromised node or relayer does not disrupt the entire transaction, safeguarding end-to-end security across networks.
In terms of end-to-end transaction security maintenance, the private relayers protect transaction data from being manipulated or intercepted, whereas the ULNs ensure secure validation.
Plus, each network component functions independently, consequently reducing the risk of system-wide vulnerabilities. This is all thanks to the resilient modular design.
Pros
- Frontrunning mitigation: Private relayers keep transactions out of public mempools.
- Fast cross-chain execution: Ultra-light nodes speed up transactions without compromising security.
- Reliable verification: Oracles ensure every transaction is correctly validated, protecting user assets.
Cons
- Complex setup: Users may initially find the architecture involving relayers and oracles difficult to grasp.
- Dependency on validators: While decentralized, LayerZero’s operation relies on validators functioning properly.
4. Chainlink CCIP: Best for securing token transfers
Chainlink’s Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) offers a reliable way to transfer tokens between blockchains while preventing transfer errors or manipulation. By verifying transactions at several points, CCIP ensures every transfer is secure from start to finish, making it an essential tool for safe cross-chain operations.
How it works?
CCIP acts like a checkpoint system for blockchain transactions. When sending tokens between networks, oracles and validators work together to confirm each step of the process.
Imagine mailing a package where each post office stamps it along the route —this ensures the package hasn’t been tampered with before it reaches its destination.
For example, if a user sends tokens from Ethereum to Avalanche, CCIP checks the transaction data at each step through oracles. Once validated, the data is passed to the receiving network’s validators. If any irregularities are found, the transaction is stopped immediately, ensuring only verified transfers succeed.
Chainlink CCIP uses multi-point validation, private communication channels, and flexible token handling for safer transfers and error prevention.
Did you know? CCIP uses automated rate limits, preventing overloading the system with large or suspicious requests.
Pros
- Frontrunning protection: Keeps transactions out of public view to prevent interference.
- Secure token transfers: Validates transactions at multiple points to prevent mistakes or loss.
- Cross-chain flexibility: Supports many networks for seamless movement of assets.
Cons
- Learning curve: Users may need time to understand programmable transfers.
- Reliance on Oracles: The process depends on validators and oracles working properly.
5. Wormhole: Best with guardian verification
Wormhole ensures that assets and data can move securely between multiple blockchains, reducing the risks involved in cross-chain transactions.
With its guardian node system, Wormhole ensures each transaction is verified independently, blocking unauthorized or tampered transfers and ensuring the transaction remains secure from start to finish.
How it works?
Wormhole functions as a bridge between blockchains, facilitating asset transfers with the help of guardian nodes. Think of the guardian nodes as checkpoints on a highway — every time a vehicle (transaction) passes through, it is inspected to ensure it meets all safety standards.
When a transaction is initiated on one blockchain, the guardian nodes validate it before it reaches the destination blockchain. If they detect any discrepancies, the transaction is rejected, ensuring that only legitimate transfers are processed. This ensures that end-to-end transaction security is maintained even when assets or data are transferred across different networks.
Wormhole is one of the few blockchain security protocols that rely on a decentralized bridge design. Plus, there is access to asset recovery tools.
Pros
- Guardian verification: Protects transfers by checking every step independently.
- Decentralized security: Reduces reliance on a single validator, preventing system-wide vulnerabilities.
- Recovery mechanisms: Provides tools for handling failed or stuck transactions.
Cons
- Bridge vulnerability risks: Like other cross-chain bridges, Wormhole is exposed to evolving attack methods.
- Complex setup: Users may need time to understand the guardian node system.
Fact check: In 2024, a vulnerability was discovered in Wormhole’s operations on the Aptos blockchain, posing a potential loss of $5 million. Fortunately, security firm CertiK identified the flaw before it could be exploited.
6. Cosmos Hub: Best for secure asset transfers using the IBC protocol
The Cosmos Hub enables secure cross-chain transactions using its Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) Protocol. It ensures that assets and data move safely between connected networks, maintaining integrity throughout the transaction. Cosmos reduces the risk of incomplete or manipulated transfers, ensuring every step — from sending to receiving — is handled securely.
How it works?
The IBC protocol functions like a secure delivery network. When a user sends tokens from one blockchain to another, IBC ensures that both chains validate the transfer before it completes. Think of it as a two-way handshake: the sending chain locks the tokens, and the receiving chain issues an equivalent amount only when the first step is confirmed. If any problem arises during the process, the transaction is halted, protecting the assets from loss.
IBC also uses Tendermint consensus to maintain trust and consistency across blockchains, ensuring that transactions are correctly validated without delays or manipulation.
Key feature: If a chain goes offline mid-transfer, IBC ensures that assets remain safe until the network recovers.
Pros
- Prevents asset loss: Two-way validation ensures that assets are never lost in transit.
- Fast and consistent: Tendermint consensus provides quick validation without compromising security.
- Resilient to downtime: IBC can handle network interruptions and secure assets until recovery.
Cons
- Network coordination: Requires coordination between multiple blockchains, which can introduce complexity.
- Limited adoption: Some networks are still integrating IBC, limiting its current use cases.
Did you know? Cosmos Hub introduced Interchain Security 2.0 (ICS 2.0), significantly enhancing the security of cross-chain transactions. This new model allows validators to select which consumer chains to secure, improving efficiency while maintaining security.
What is end-to-end transaction security?
End-to-end transaction security ensures that every transaction, from initiation to completion, is protected from risks like manipulation, frontrunning, or incomplete execution.
Quick example: In 2024, Uniswap faced persistent frontrunning attacks, where MEV (Maximal Extractable Value) bots executed sandwich attacks by placing transactions before and after legitimate trades. These bots profited by exploiting price changes caused by unsuspecting users’ trades.
This concept guarantees that no unauthorized entity can interfere with or alter a transaction, providing users with complete confidence in their blockchain activities.
Without proper end-to-end security, blockchain transactions risk exposure to frontrunning, phishing, or incomplete transfers.
2024 even saw a related phishing attack where a campaign targeted liquidity providers (LPs) of Uniswap V3, stealing over $4.7 million in ETH. Attackers sent malicious tokens to users disguised as legitimate airdrops, tricking them into interacting with fake interfaces that drained their wallets.
Blockchain security protocols ensure users’ funds remain safe, interactions with smart contracts are trustworthy, and data is not leaked or manipulated along the way.
Is it enough to secure transactions with blockchain security protocols?
Blockchain security protocols are a critical step toward safe transactions. However, they may not be enough on their own. While these protocols provide end-to-end security by preventing manipulation and verifying data, evolving threats require continuous upgrades.
A multi-layered approach — including user awareness, audits, and additional safeguards — ensures stronger security and trust across decentralized networks.
Frequently asked questions
What makes blockchain security protocols essential for end-to-end transaction security?
Are blockchain security protocols alone enough to protect transactions?
Which blockchain protocols offer reliable end-to-end security in 2025?
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, the educational content on this website is offered in good faith and for general information purposes only. BeInCrypto prioritizes providing high-quality information, taking the time to research and create informative content for readers. While partners may reward the company with commissions for placements in articles, these commissions do not influence the unbiased, honest, and helpful content creation process. Any action taken by the reader based on this information is strictly at their own risk. Please note that our Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers have been updated.




