Entering 2024, with AI emerging as a new cornerstone of crypto narratives, the idea of AI-centric asset issuance has carved out new pathways for creative exploration. BeInCrypto sat down with ORA Protocol’s founder, Kartin Wong, to discuss the Initial Model Offering (IMO). This novel concept has already attracted widespread attention and has the potential to become a new industry standard.
The ORA Protocol (formerly known as HyperOracle) is a verifiable oracle protocol that brings AI and complex computation on-chain. ORA expands the capabilities of smart contracts by integrating richer data sources and computing power, enabling developers to innovate without constraints. ORA’s solutions have gained the trust of various entities, including Compound, Ethereum Foundation, Optimism, and Polygon.
New Era in AI Development
Historically, AI development has been shackled by a monolithic approach to monetization, heavily reliant on proprietary models and subscription-based services. This model restricts the free exchange of ideas and places significant financial and resource-based barriers for developers. Wong’s ORA vision addresses the critical challenges AI innovators face — primarily, the monetization and accessibility of AI models.
«The biggest issue with AI models today is that they’re not yet powerful enough to fully solve the problems they’re meant to tackle. For widespread use, the technology has to be top-notch, like ChatGPT, which required hundreds of millions of dollars in investment to develop a high-performing language model. Most AI companies, especially within their specific fields, struggle with not having enough funds to launch their products successfully. This lack of funding is a significant barrier for many AI companies wanting to bring their products to market».
Recognizing the need for a new model that balances open-source collaboration with financial viability, ORA has introduced the concept of “IMO”, which stands for Initial Model Offering. At its essence, the premise of IMO is clear. If tokenization applies to everything, then AI models are no outliers and can be tokenized for asset issuance. This allows creators to recoup their investment and potentially profit directly from their developments.
For instance, after investing $5m in a high-quality AI model, a creator might open-source it to enhance its capabilities. By tokenizing the model and offering the tokens for sale immediately upon launch or selling a majority to the community, creators can anticipate a rise in token value. This strategy promptly returns significant liquidity to the model’s creator after the launch of a successful model.
From the users’ point of view, such a tool also looks very attractive. Individuals who have confidence in a specific AI model can invest in its associated token. Should the model yield economic gains from its application, investors may receive a share of those benefits.
«For example, I put down an AI model on-chain, and every time a smart contract or user wants to use it, they pay me like 0.01 ETH. After a week, about 10 000 people call it on-chain, so the income for the protocol is now 100 ETH in a week. This ETH will go to the model’s token holders according to the size of their investment».
ORA Protocol’s founder stresses the importance of educating people on IMOs and their impact on AI project funding. When a model offering is successful, and the value of its token rises sharply, it draws people’s attention. This increases interest and investment in future IMOs, boosting liquidity in the AI sector.
Understanding the Paradigm Shift
Kartin acknowledges the journey toward a fully decentralized and permissionless ecosystem is fraught with technical challenges. These include ensuring model integrity, maintaining performance standards, and achieving true decentralization without compromising user trust or model quality.
ORA tackles hurdles using two ERC standards, ERC-7641 and ERC-7007, alongside their onchain AI oracle. Let’s look at each of these components separately.
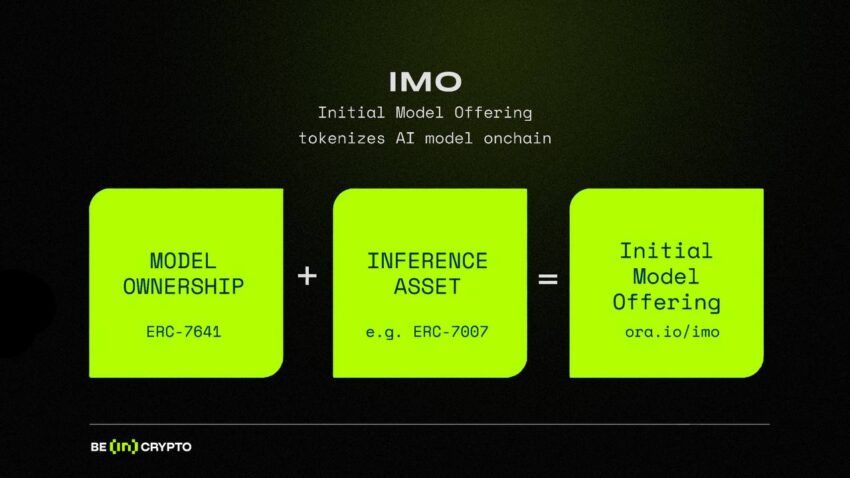
- ERC-7641 is a token standard compatible with ERC-20. To launch an IMO, developers link the model to an ERC-7641 asset and set token numbers in the smart contract. Investors buy these tokens, gaining ownership in the AI model proportional to their token share, similar to shareholders. The ERC-7641 protocol sets profit distribution rules in the contract, enabling automatic profit sharing based on token holdings.
- ERC-7007 is a token standard for AI-generated content, safeguarding authenticity and origin traceability. It maintains AI-generated content metadata on the blockchain and uses smart contracts for automatic verification. Developers can apply technologies like zkML or opML to confirm if the AI-generated content (AIGC) for a specific NFT truly originates from a certain machine learning model and inputs.
- ORA’s Onchain AI Oracle authenticates and operationalizes AI models on the blockchain, ensuring the deployment and functioning of AI models occur entirely on-chain and enhancing the transparency and authenticity of their operational process.

ORA has also integrated an additional Optimistic Machine Learning (opML) technology. AI models frequently represent crucial competitive advantages, and fully revealing them could undermine their commercial value — opML can employ zero-knowledge proofs or similar cryptographic techniques to confirm the accuracy of the model’s results without revealing the model’s details. This method maintains the model’s credibility and efficiency while protecting its confidentiality and unique advantage.
Nevertheless, Kartin recognizes that the protocol still has a lot of work to do to achieve its main goal.
«The major problem of tokenizing AI models is that we want it to be permissionless and fully decentralized. We spent 18 months on the R&D to make it a real thing; it’s very revolutionary. But the problem is that we are the only ones that can operate an opML library because we invented it. So right now, if you want to tokenize an AI model, you have to go through ORA protocol — we take the model, cross-compile it and then share the Docker image to all the nodes, etc. In the future, we will make it fully decentralized and permissionless. Right now, it’s decentralized, but it’s not fully permissionless».
Ethical Implications and the Path to Regulatory Alignment
Tokenizing AI models raises significant ethical questions, particularly concerning misuse and accountability. ORA Protocol approaches these challenges with a dual strategy focusing on ethical guidelines and regulatory compliance. Kartin emphasizes the importance of creating a governance framework that aligns with global standards, making sure that the potential of tokenized AI models does not outpace societal and regulatory norms.
«The biggest ethical challenge in IMO is that, actually, it’s not IMO itself. It’s actually the AI Oracle. Once you put an AI model on the blockchain, it cannot be shut down as long as people use it. So it will raise some concerns — for example, people can generate unethical content with an AI model. But blockchain itself has the same concerns. Some people use it to launder money and you have no way to stop it. Once you do it on Bitcoin or Ethereum, it’s fully decentralized. Then you just have no control on it».
ORA’s founder notes that when an AI model company undertakes an IMO, they ensure full compliance by tokenizing their model, which is not classified as a security, particularly adhering to regulations in the United States. The approach is to have each AI company, regardless of their global location, assume responsibility for compliance due to the varying laws and regulations across different countries. Since the primary beneficiary of an IMO is the AI company itself, it falls upon them to navigate and adhere to the specific legal frameworks of their respective countries.
As for example, Singapore’s regulations on AI and tokenization may differ significantly from those in the U.S., requiring companies in Singapore to independently manage and mitigate any potential ethical concerns related to their AI models. This could involve implementing governance mechanisms within the tokens or embedding a blacklist in the smart contract to prevent unethical uses of the AI model. This principle of localized responsibility and compliance applies universally across all jurisdictions.
New Industry Standard
The current intersection of cryptocurrency narratives with the AI sector stems from AI’s impact on production. This convergence is particularly relevant because blockchain technology can address two significant challenges within the AI industry. The first is liquidity, which Initial Model Offerings (IMO) have begun to tackle by providing a platform for financing AI models. The second challenge involves ensuring transparency to prevent IMOs from being perceived as opaque or untrustworthy. Utilizing blockchain technology can verify the authenticity of these offerings, helping to solve issues of trust and transparency.
Kartin firmly believes that all industries utilizing AI in their production processes will see advantages from tokenized AI models, particularly through what is referred to as an ”on-chain supervisor”. This concept addresses a common issue in AI production models — not the fear of AI turning against humans but the frequent occurrence of operational glitches. A larger language model (LLM) detects and resolves such glitches. If a user suspects a glitch, they can report the issue to this LLM, assessing whether the original AI model is experiencing a glitch.
The most effective supervisor for this purpose exists on the blockchain. Despite the higher cost, the key advantage is that this supervisory AI model is operational around the clock, ensuring constant performance monitoring of AI models deployed in local devices. Therefore, every AI model that operates locally could benefit from being linked to a tokenized, on-chain AI model that serves as a perpetual supervisor.
In his closing thoughts, Kartin notes the enthusiasm surrounding the AI crypto space is expected to continue as long as new developments and breakthroughs exist. Given these dynamics, the momentum within the AI sector, fueled by both advancements and the integration with blockchain, is likely to sustain for a considerable period.
«AI is here to stay, and what we’re doing here is resolving the major concern of all AI companies in the world. So this will bring tons of value into crypto and also tons of value to all the AI companies. I think IMO will be the story of the year, of the whole cycle. I think after this year, it will 100% become the industry standard to do things, to launch an AI model».
Disclaimer
In compliance with the Trust Project guidelines, this opinion article presents the author’s perspective and may not necessarily reflect the views of BeInCrypto. BeInCrypto remains committed to transparent reporting and upholding the highest standards of journalism. Readers are advised to verify information independently and consult with a professional before making decisions based on this content. Please note that our Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers have been updated.


