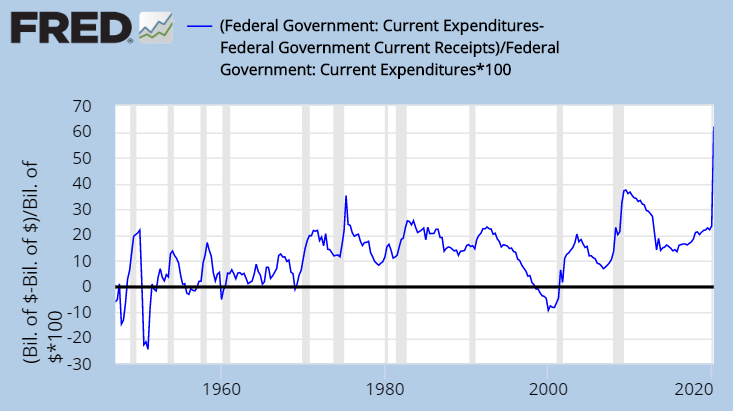
Over the past 50 years, the cost of living has skyrocketed, raising concerns about whether our current economic trajectory leads to hyperinflation. As prices continue to soar, many are turning to alternative solutions like Bitcoin to protect their wealth and safeguard against the potential collapse of traditional financial systems.
As we witness a shifting global financial landscape, the struggle between hyperinflationary fiat currencies and the disruptive force of digital assets like Bitcoin grows increasingly apparent. With both sides vying for supremacy, it’s crucial to grasp the key distinctions and driving factors that set them apart.
A Tale of Two Currencies
The specter of hyperinflation looms large, with notorious examples such as Zimbabwe and Venezuela etched in recent memory. These economic disasters highlight the vulnerability of fiat currencies to the whims of government policies and excessive money printing.
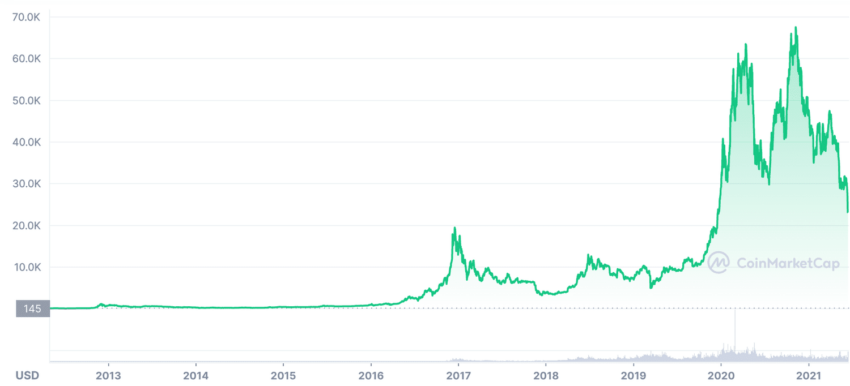
Meanwhile, Bitcoin’s finite supply of 21 million coins has positioned it as a digital alternative to gold. Its decentralized nature provides insulation from the monetary policies that contribute to hyperinflation, making it an attractive option for those seeking a hedge. Furthermore, Bitcoin’s global acceptance and increasing institutional interest have cemented its status as a viable contender against traditional currencies.
The Zimbabwean Nightmare
In the late 2000s, Zimbabwe experienced one of history’s worst cases of hyperinflation. At its peak, prices doubled every 24 hours, rendering the local currency virtually worthless. The underlying causes included political instability, rampant corruption, and a series of misguided economic policies, such as the seizure of commercial farms and excessive money printing to pay government debts.
In contrast, the value of Bitcoin has grown exponentially since its inception in 2009. Although it has experienced volatile price swings, it has ultimately proven to be a more stable store of value than the Zimbabwean dollar. Today, an increasing number of Zimbabweans are adopting cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin to circumvent the country’s economic challenges and access global markets.
Venezuela’s Cryptocurrency Lifeline
Venezuela’s ongoing economic crisis has led to widespread hyperinflation, with the Bolivar’s value plummeting by over 99% in just a few years. In response, many Venezuelans have turned to Bitcoin as a means of preserving their wealth and conducting transactions beyond the reach of government control. They have used the cryptocurrency to purchase essential goods and services, remit money abroad, and even pay employees.
Remarkably, Venezuela now ranks among the top countries in terms of Bitcoin adoption. This demonstrates the cryptocurrency’s potential to serve as a lifeline in the face of economic turmoil. The government has even launched its own digital currency, the Petro, in a bid to circumvent international sanctions and stabilize the economy.
A Digital Refuge for the Argentine Peso
Argentina, too, has grappled with chronic inflation, which hit 94.8% in 2022. In an effort to protect their savings, many Argentinians have embraced Bitcoin as a viable alternative to the beleaguered peso. This trend reflects a growing recognition of the cryptocurrency’s ability to shield wealth from the ravages of hyperinflation.
Additionally, the Argentine government has imposed strict capital controls, making it difficult for citizens to access foreign currencies. Bitcoin’s decentralized nature allows Argentinians to bypass these restrictions and access the global economy, further solidifying its appeal as an alternative to fiat currency.

Bitcoin’s Achilles Heel
For all its apparent advantages, Bitcoin is not without its drawbacks. The cryptocurrency’s volatile price fluctuations can pose risks for those seeking to preserve wealth. Additionally, the relatively slow transaction speeds and high fees may deter some potential adopters.
Moreover, governments and central banks are clamping down on cryptocurrencies in an attempt to preserve their monetary authority.
Such actions could hinder Bitcoin’s adoption and hamper its ability to serve as a hedge against hyperinflation. For example, China’s strict measures against crypto trading and mining have significantly disrupted the global market.
Another issue is the environmental impact of Bitcoin mining. The energy-intensive process draws criticism for its substantial carbon footprint, prompting some governments to consider measures to curb large-scale mining.
The Intersection of Traditional and Digital Finance
As living costs surge, attention is drawn to the potential of Bitcoin to act as a shield against hyperinflation. Yet, Bitcoin’s long-term success remains to be seen, highlighting the importance of adopting sound economic policies and responsible monetary management.
This convergence of traditional finance and cryptocurrencies signals a pivotal moment in global finance. As central banks venture into creating their own digital currencies, or CBDCs, the financial landscape prepares for a significant shift, transforming the way we perceive and manage money.
Charting the Future
As the world confronts escalating living costs, Bitcoin emerges as a potential safeguard for individuals seeking protection from hyperinflation’s damaging effects. While cryptocurrencies offer promising solutions, the journey ahead is filled with challenges such as regulatory constraints and environmental concerns. The financial well-being of countless individuals depends on successfully addressing these issues as we navigate the evolving financial landscape.
Disclaimer
Following the Trust Project guidelines, this feature article presents opinions and perspectives from industry experts or individuals. BeInCrypto is dedicated to transparent reporting, but the views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect those of BeInCrypto or its staff. Readers should verify information independently and consult with a professional before making decisions based on this content. Please note that our Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers have been updated.


